SLAAE72 December 2022 MSPM0L1105 , MSPM0L1106 , MSPM0L1303 , MSPM0L1304 , MSPM0L1304-Q1 , MSPM0L1305 , MSPM0L1305-Q1 , MSPM0L1306 , MSPM0L1306-Q1 , MSPM0L1343 , MSPM0L1344 , MSPM0L1345 , MSPM0L1346
2.1.1 Power Domains and Power Modes
To realize different power levels, two core power domains are provided on the device: PD1 and PD0 and five operating modes (power modes) are provided to optimize the device power decreasing power: RUN, SLEEP, STOP, STANDBY, and SHUTDOWN. Figure 2-1 indicates what domains are available in each operating mode of the device.
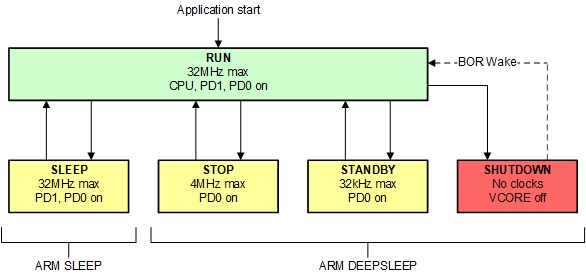 Figure 2-1 MSPM0Lxx Operating Modes
Figure 2-1 MSPM0Lxx Operating ModesA more detailed supported functionality in each operating mode is given in Table 2-1. Users can choose a suitable working condition according to your applications for the limited need to the clock frequency, wake sources, CPU and peripherals requirements.
Abbreviations used in Table 2-1:
EN: The function is enabled in the specified mode.
DIS: The function is disabled in the specified mode, but the function's configuration is retained.
OPT: The function is optional in the specified mode, and remains enabled if configured to be enabled.
NS: The function is not automatically disabled in the specified mode, but its use is not supported.
OFF: The function is powered off in the specified mode, and no configuration information is retained.
| Operating Mode | RUN | SLEEP | STOP | STANDBY | SHUTDOWN | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUN0 | RUN1 | RUN2 | SLEEP0 | SLEEP1 | SLEEP2 | STOP0 | STOP1 | STOP2 | STANDBY0 | STANDBY1 | |||
| Oscillators | SYSOSC | EN | EN | DIS | EN | EN | DIS | OPT | EN | DIS | DIS | DIS | OFF |
| LFOSC | EN | OFF | |||||||||||
| Clocks | CPUCLK | 32 MHz max | 32 kHz | 32 kHz | DIS | OFF | |||||||
| MCLK to PD1 | 32 MHzM max | 32 kHz | 32 kHz | 32 MHz max | 32 kHz | 32 kHz | DIS | OFF | |||||
| ULPCLK to PD0 | 32 MHz max | 32 kHz | 32 kHz | 32 MHz max | 32 kHz | 32 kHz | 4 MHz max | 4 MHz | 32 kHz | DIS | OFF | ||
| ULPCLK to TIMG0/1 | 32 MHz max | 32 kHz | 32 kHz | 32 MHz max | 32 kHz | 32 kHz | 4 MHz max | 4 MHz | 32 kHz | OFF | |||
| MFCLK | OPT | DIS | OPT | DIS | OPT | DIS | OFF | ||||||
| LFCLK | 32 kHz | DIS | OFF | ||||||||||
| LFCLK to TIMG0/1 | 32 kHz | OFF | |||||||||||
| MCLK Monitor | OPT | DIS | OFF | ||||||||||
| PMU | POR monitor | EN | |||||||||||
| BOR monitor | EN | OFF | |||||||||||
| Core regulator | FULL DRIVE | REDUCED DRIVE | LOW DRIVE | OFF | |||||||||
| Core Functions | CPU | EN | DIS | OFF | |||||||||
| DMA | OPT |
DIS (triggers supported) |
OFF | ||||||||||
| Flash | EN | OPT | DIS | OFF | |||||||||
| SRAM | EN | OPT | DIS | OFF | |||||||||
| Peripherals | PD1 Peripherals | OPT | DIS or OFF (peripheral dependent) | OFF | |||||||||
| PD0 Peripherals | OPT | OPT | OFF | ||||||||||
| Analog | ADC | OPT |
NS (triggers supported) |
OFF | |||||||||
| OPA | OPT | NS | OPT | NS | OPT | NS | OFF | ||||||
| GPAMP | OPT | NS | OFF | ||||||||||
| COMP / 8-bit DAC | OPT | OPT (ULP only) | OPT | OPT (ULP only) | OPT | OPT (ULP only) | OFF | ||||||
| IOMUX and IO Wakeup | EN | DIS with WAKE | |||||||||||
| Wake Sources | N/A | ANY IRQ | PD0 IRQ | IOMUX, NRST | |||||||||