SLAAE75A November 2022 – March 2023 MSPM0L1105 , MSPM0L1106 , MSPM0L1303 , MSPM0L1304 , MSPM0L1304-Q1 , MSPM0L1305 , MSPM0L1305-Q1 , MSPM0L1306 , MSPM0L1306-Q1 , MSPM0L1343 , MSPM0L1344 , MSPM0L1345 , MSPM0L1346
3.1 Digital Power Supply
The device has five reset levels:
- Power-on reset (POR)
- Brown-out reset (BOR)
- Boot reset (BOOTRST)
- System reset (SYSRST)
- CPU reset (CPURST)
The details of the relationships between reset levels is described in the MSPM0 L-Series 32-MHz Microcontrollers Technical Reference Manual.
After a cold start, the NRST pin is configured in NRST mode. The NRST pin must be high for the device to boot successfully. There is no internal pullup resistor on NRST. External circuitry (either a pullup resistor to DVCC or a reset control circuit) must actively pull NRST high for the device to start. A capacitor and an open button are needed for manual reset (see #FIG_GLC_3KH_GVB). After the device is started, a low pulse on NRST that is <1 second in duration triggers a BOOTRST. If a low pulse on NRST is held for >1 second, a POR is triggered.
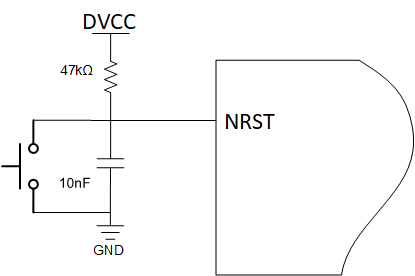 Figure 3-1 NRST Recommended Circuit
Figure 3-1 NRST Recommended Circuit