SLVAFX0 October 2024 TLV702 , TLV703 , TLV755P , TPS74401 , TPS7A13 , TPS7A14 , TPS7A20 , TPS7A21 , TPS7A49 , TPS7A52 , TPS7A53 , TPS7A53B , TPS7A54 , TPS7A57 , TPS7A74 , TPS7A83A , TPS7A84A , TPS7A85A , TPS7A91 , TPS7A92 , TPS7A94 , TPS7A96 , TPS7H1111-SP
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction to linear regulator turn-on time
-
2What impacts the LDO rise time?
- 2.1
Simple Use Cases
- 2.1.1 Case 1: LDO with an NR filter but without CFF capacitance
- 2.1.2 Case 2: NR filter with a CFF capacitance
- 2.1.3 Fast-charge circuitry
- 2.1.4
Non-ideal LDO behavior
- 2.1.4.1 Applied voltage bias
- 2.1.4.2 Fast charge current tolerance
- 2.1.4.3 Internal error amplifier offset voltage
- 2.1.4.4 Temperature impacts the fast-charge current source
- 2.1.4.5 Error amplifier common mode voltage
- 2.1.4.6 Reference voltage (VREF) ramp time dominates the turn-on time
- 2.1.4.7 Start-up during dropout mode
- 2.1.4.8 Large values of COUT induce internal current limit
- 2.1.4.9 Limitations of large-signal LDO bandwidth
- 2.2 Specific Use Cases and Examples
- 2.1
Simple Use Cases
- 3System Considerations
- 4LDO regulators referenced in this paper
- 5Conclusion
- 6References
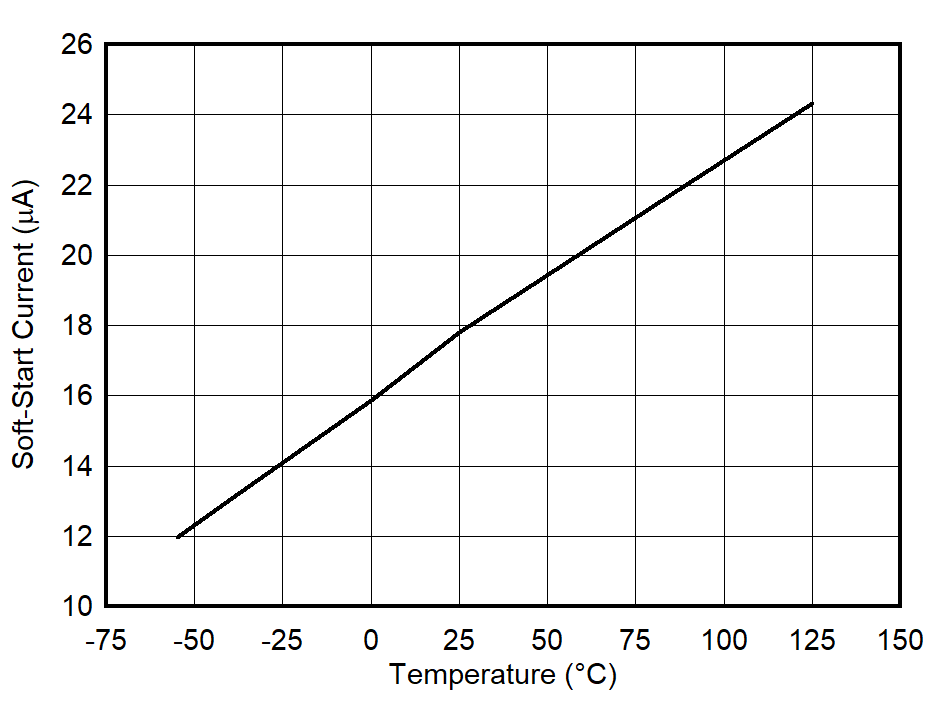
2.1.4.4 Temperature impacts the fast-charge current source
The LDO regulator die temperature momentarily increases during turn on as a result of transient power dissipation while the device charges the output capacitor COUT. This temporary increase in junction temperature can slightly change the proportional to absolute temperature (PTAT) current source used as the soft-start current source in some devices. Characterization graphs and associated test conditions such as Figure 2-7 are usually included in the device data sheet. During initial turn-on, the higher power dissipation can cause the current source to increase slightly. Near the end of the turn-on period, the power dissipation decreases, which can cause the current source to decrease. Figure 2-8 shows this behavior as a slight curvature in the start-up waveform.
| CIN = COUT = 10μF | CBIAS = 1μF | CSS = 0nF |
| VBIAS = VIN = 6V | VOUT = 0.65V | VEN = 1.5V |
| IOUT = 0A | from the TPS7A74 data sheet | |
