SLVU944B October 2015 – October 2020 TPS7H1101-SP
3.3.3 High-Side Current Sense
Monitoring the voltage at the CS pin will indicate voltage proportional to the output current. Figure 3-4 shows typical curve VCS vs IOUT for Vin = 2.28 V and R23 = 3.65 kΩ. A resistor connected from current sense (CS) pin to VIN indicates voltage proportional to the output current.
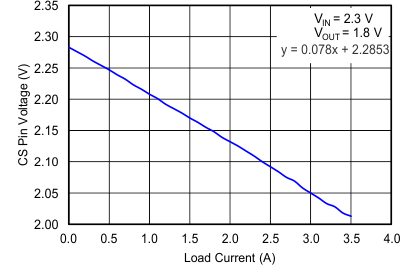 Figure 3-4 VCS (V) vs IOUT (A)
Figure 3-4 VCS (V) vs IOUT (A)Monitoring current in CS pin (ICS vs IOUT) indicates the current sense ratio between the main PMOSFET and the current sense MOSFET as shown in Figure 3-5. This plot shows that the CSR ratio is independent of VCS voltage. Note that VCS must be above 0.3V to insure proper biasing, and also must be greater than 0.9 x VREF (0.544 V) to have foldback current limit enabled.
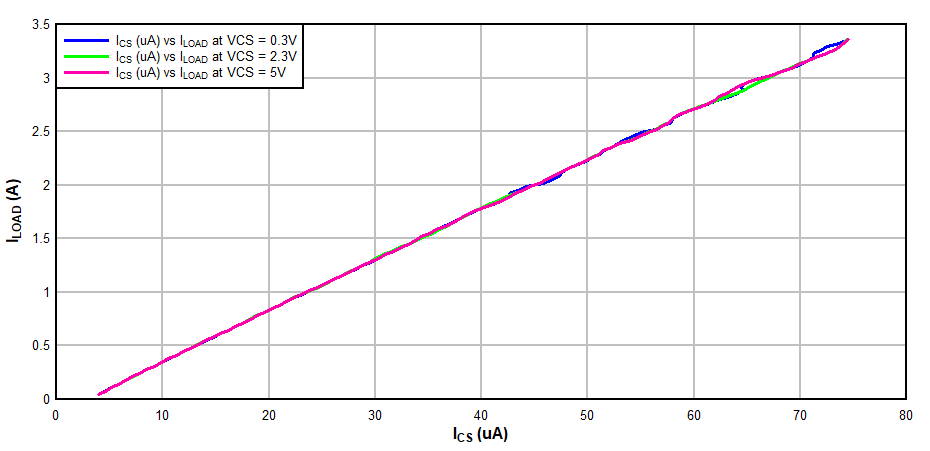 Figure 3-5 IOUT (A) vs ICS (A)
Figure 3-5 IOUT (A) vs ICS (A)