SBAS771D June 2017 – October 2024 AMC1303E0510 , AMC1303E0520 , AMC1303E2510 , AMC1303E2520 , AMC1303M0510 , AMC1303M0520 , AMC1303M2510 , AMC1303M2520
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Power Ratings
- 6.6 Insulation Specifications
- 6.7 Safety-Related Certifications
- 6.8 Safety Limiting Values
- 6.9 Electrical Characteristics: AMC1303x05x
- 6.10 Electrical Characteristics: AMC1303x25x
- 6.11 Switching Characteristics
- 6.12 Timing Diagrams
- 6.13 Insulation Characteristics Curves
- 6.14 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DWV|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6.9 Electrical Characteristics: AMC1303x05x
minimum and maximum specifications apply from TA = –40°C to +125°C,
AVDD = 3.0V to 5.5V, DVDD = 2.7V to 5.5V, AINP = –50mV to 50mV, AINN = AGND, and
sinc3 filter with OSR = 256 (unless otherwise noted); typical
specifications are at TA = 25°C, AVDD = 5V, and DVDD = 3.3V
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANALOG INPUTS | ||||||
| VClipping | Differential input voltage before clipping output | VIN = AINP – AINN | ±64 | mV | ||
| FSR | Specified linear differential full-scale | VIN = AINP – AINN | –50 | 50 | mV | |
| Absolute common-mode input voltage(1) | (AINP + AINN) / 2 to AGND | –2 | AVDD | V | ||
| VCM | Operating common-mode input voltage | (AINP + AINN) / 2 to AGND | –0.032 | AVDD – 2.1 | V | |
| VCMov | Common-mode overvoltage detection level | (AINP + AINN) / 2 to AGND | AVDD – 2 | V | ||
| Hysteresis of the common-mode overvoltage detection level | 90 | mV | ||||
| CIN | Single-ended input capacitance | AINN = AGND | 4 | pF | ||
| CIND | Differential input capacitance | 2 | pF | |||
| RIN | Single-ended input resistance | AINN = AGND | 4.75 | kΩ | ||
| RIND | Differential input resistance | 4.9 | kΩ | |||
| IIB | Input bias current | AINP = AINN = AGND, IIB = IIBP + IIBN | –97 | –72 | –57 | μA |
| IIO | Input offset current | ±10 | nA | |||
| CMTI | Common-mode transient immunity | 50 | 100 | kV/µs | ||
| CMRR | Common-mode rejection ratio | AINP = AINN, fIN = 0Hz, VCM min ≤ VIN ≤ VCM max | –99 | dB | ||
| AINP = AINN, fIN from 0.1Hz to 50kHz, VCM min ≤ VIN ≤ VCM max | –98 | |||||
| PSRR | Power-supply rejection ratio | AINP = AINN = AGND, 3.0V
≤ AVDD ≤ 5.5V, at dc |
–108 | dB | ||
| AINP = AINN = AGND, 3.0V
≤ AVDD ≤ 5.5V, 10kHz, 100mV ripple |
–107 | |||||
| BW | Input bandwidth(2) | AMC1303x0510 | 430 | kHz | ||
| AMC1303x0520 | 800 | |||||
| DC ACCURACY | ||||||
| DNL | Differential nonlinearity | Resolution: 16 bits | –0.99 | 0.99 | LSB | |
| INL | Integral nonlinearity(3) | Resolution: 16 bits | –4 | ±1 | 4 | LSB |
| EO | Offset error | Initial, at TA = 25°C, AINP = AINN = AGND | –50 | ±2.5 | 50 | µV |
| TCEO | Offset error thermal drift(4) | –1 | ±0.25 | 1 | µV/°C | |
| EG | Gain error | Initial, at TA = 25°C | –0.2% | ±0.005% | 0.2% | |
| TCEG | Gain error thermal drift(5) | –40 | ±20 | 40 | ppm/°C | |
| AC ACCURACY | ||||||
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio | AMC1303x0510, fIN = 35Hz | 81 | 84 | dB | |
| AMC1303x0520, fIN = 35Hz | 79 | 83 | ||||
| THD | Total harmonic distortion | fIN = 35Hz | –97 | –86 | dB | |
| SFDR | Spurious-free dynamic range | AMC1303x0510, fIN = 35Hz | 96 | dB | ||
| AMC1303x0520, fIN = 35Hz | 97 | |||||
| DIGITAL OUTPUTS (CMOS Logic) | ||||||
| CLOAD | Output load capacitance | 30 | pF | |||
| VOH | High-level output voltage | IOH = –20µA | DVDD – 0.1 | V | ||
| IOH = –4mA | DVDD – 0.4 | |||||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | IOL = 20µA | 0.1 | V | ||
| IOL = 4mA | 0.4 | |||||
| POWER SUPPLY | ||||||
| IAVDD | High-side supply current | AMC1303x0510, 3.0V ≤ AVDD ≤ 3.6V | 5.4 | 7.3 | mA | |
| AMC1303x0510, 4.5V ≤ AVDD ≤ 5.5V | 6.0 | 8.0 | ||||
| AMC1303x0520, 3.0V ≤ AVDD ≤ 3.6V | 6.3 | 8.5 | ||||
| AMC1303x0520, 4.5V ≤ AVDD ≤ 5.5V | 7.2 | 9.8 | ||||
| IDVDD | Controller-side supply current | AMC1303E0510, 2.7V ≤
DVDD ≤ 3.6V, CLOAD = 15pF |
3.3 | 4.5 | mA | |
| AMC1303E0510, 4.5V ≤
DVDD ≤ 5.5V, CLOAD = 15pF |
3.6 | 5.0 | ||||
| AMC1303M0510, 2.7V ≤
DVDD ≤ 3.6V, CLOAD = 15pF |
3.5 | 4.7 | ||||
| AMC1303M0510, 4.5V ≤
DVDD ≤ 5.5V, CLOAD = 15pF |
3.9 | 5.4 | ||||
| AMC1303E0520, 2.7V ≤
DVDD ≤ 3.6V, CLOAD = 15pF |
4.1 | 5.5 | ||||
| AMC1303E0520, 4.5V ≤
DVDD ≤ 5.5V, CLOAD = 15pF |
4.7 | 6.5 | ||||
| AMC1303M0520, 2.7V ≤
DVDD ≤ 3.6V, CLOAD = 15pF |
4.6 | 6.0 | ||||
| AMC1303M0520, 4.5V ≤
DVDD ≤ 5.5V, CLOAD = 15pF |
5.4 | 7.2 | ||||
(1) Steady-state voltage supported by the device in case of a system failure. See
the specified common-mode input voltage VCM for normal operation.
Observe analog input voltage range as specified in the Absolute Maximum Ratings table.
(2) This parameter is the –3dB, second-order, roll-off frequency of the integrated
differential input amplifier to consider for antialiasing filter designs.
(3) Integral nonlinearity is defined as the maximum deviation from a straight line passing through the end-points of the ideal ADC transfer function expressed as number of LSBs or as a percent of the specified linear full-scale range FSR.
(4) Offset error drift is calculated using the box method as described by the following equation: 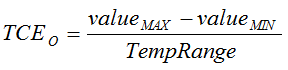 .
.
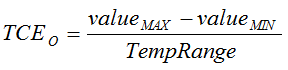 .
.(5) Gain error drift is calculated using the box method as described by the following equation:  .
.
 .
.