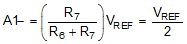SBOS392H August 2007 – August 2019 REF3312 , REF3318 , REF3320 , REF3325 , REF3330 , REF3333
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
-
10Applications and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Applications
- 10.2.1
REF3312 in a Bipolar Signal-Chain Configuration
- 10.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 10.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 10.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 10.2.1
REF3312 in a Bipolar Signal-Chain Configuration
- 11Power-Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
10.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
Figure 19 depicts a simplified schematic for this design showing the MSP430 ADC inputs and full input conditioning circuitry. The ADC is configured for a bipolar measurement where final conversion result is the differential voltage, VDIFF, between the positive and negative ADC inputs, A1+ and A1–. The bipolar, ground-referenced input signal must be level-shifted and attenuated by the op amp so that the output is biased to VREF / 2 and has a differential voltage that is within the ±VREF / 2 input range of the ADC. The transfer function for the op-amp circuit simplifies to Equation 4.
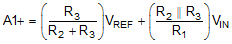
where
- R1 = R4
- R5 = R2 || R3
The voltage applied to the negative ADC input, A1–, is based on the resistor divider formed by R6 and R7 and is set to VREF / 2 by setting R6 equal to R7, as shown in Equation 5.