-
TPS6208x 1.2A高効率降圧型コンバータ、 DCS-Control およびスヌーズ・モード搭載
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 13メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
- 重要なお知らせ
TPS6208x 1.2A高効率降圧型コンバータ、 DCS-Control およびスヌーズ・モード搭載
1 特長
2 アプリケーション
- バッテリ駆動の携帯機器
- ポイント・オブ・ロード・レギュレータ
- システム電源レールの電圧変換
3 概要
TPS6208xデバイスは、高周波数の同期整流降圧型コンバータのファミリです。入力電圧範囲が2.3V~6Vで、一般的なバッテリ・テクノロジをサポートします。または、このデバイスを低電圧のシステム電源レールとしても使用できます。
TPS6208xは、広い出力電流範囲にわたって高効率の降圧型変換を行うことに特化しています。中負荷から重負荷ではPWMモードで動作し、軽負荷電流時には自動的にパワーセーブ・モードへ移行するため、負荷電流のあらゆる範囲にわたって高効率が維持されます。非常に小さい負荷から無負荷電流時まで高い効率を維持するために、静止電流の非常に低いスヌーズ・モードが実装されています。この機能はMODEピンによって有効化され、バッテリ駆動アプリケーションの稼働時間を延ばし、スタンバイ電流を最低レベルに維持することで、低いスタンバイ電流を目標としたグリーン・エネルギーの基準を満たしています。
システム電源レールの要件に対応するため、内部のループ補償によって100µFを超える外部出力コンデンサを幅広い選択肢から選ぶことができます。 DCS-Control™アーキテクチャにより、優れた負荷過渡性能と出力電圧レギュレーション精度を実現しています。このデバイスは、2mm×2mmのサーマル・パッド付きWSONパッケージで供給されます。
製品情報(1)
| 型番 | パッケージ | 本体サイズ(公称) |
|---|---|---|
| TPS62080 | WSON (8) | 2.00mm×2.00mm |
| TPS62080A | ||
| TPS62081 | ||
| TPS62082 |
- 提供されているすべてのパッケージについては、データシートの末尾にある注文情報を参照してください。
代表的なアプリケーションの回路図 |
|
|
space 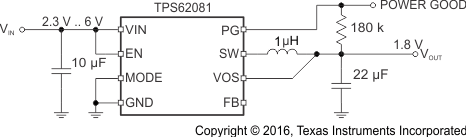 |
4 改訂履歴
Changes from E Revision (April 2015) to F Revision
- Changed From: TA = –40°C to 85°C To: TJ = –40°C to 125°C in the Electrical Characteristics condition statementGo
- Added a Test Condition to ISD in the Electrical Characteristics Go
- Changed the RDS(on) High-side TYP value From: 120 mΩ To: 95 mΩ in the Electrical CharacteristicsGo
- Changed the RDS(on) Low-side TYP value From: 90 mΩ To: 70 mΩ in the Electrical CharacteristicsGo
- Changed the graphs to include a 125°C curve in the Typical Characteristics Go
- Added 50 Ω value to the Power Good block in Figure 5Go
- Added 50 Ω value to the Power Good block in Figure 6Go
- Added Table 1 Go
Changes from D Revision (July 2013) to E Revision
- Added 「ピン構成および機能」セクション、「ESD定格」表、「機能説明」セクション、「デバイスの機能モード」セクション、「アプリケーションと実装」セクション、「電源に関する推奨事項」セクション、「レイアウト」セクション、「デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート」セクション、「メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報」セクションGo
Changes from C Revision (May 2013) to D Revision
- Deleted TPS62080ADGN from ORDERING INFORMATION tableGo
- Deleted TPS62080A column from the Thermal Information tableGo
Changes from B Revision (March 2012) to C Revision
- Changed the Thermal Information tables valuesGo
Changes from A Revision (February 2012) to B Revision
- Changed TPS62080ADSG from Product Preview to Production Data in ORDERING INFORMATIONGo
Changes from * Revision (September 2011) to A Revision
5 Device Comparison Table
| PART NUMBER(2) | OUTPUT VOLTAGE(1) | OUTPUT DISCHARGE RESISTOR | PACKAGE MARKING | PACKAGE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPS62080DSG | Adjustable | 1 kΩ | QVR | 8-Pin WSON |
| TPS62081DSG | 1.8 V | 1 kΩ | QVS | 8-Pin WSON |
| TPS62082DSG | 3.3 V | 1 kΩ | QVT | 8-Pin WSON |
| TPS62080ADSG | Adjustable | 40 Ω | SBN | 8-Pin WSON |
6 Pin Configuration and Functions
space

space
space
Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| EN | 1 | IN | Device Enable Logic Input. Logic HIGH enables the device, logic LOW disables the device and turns it into shutdown. Do not leave floating. |
| GND | 2 | PWR | Power and Signal Ground. |
| MODE | 3 | IN | Snooze Mode Enable Logic Input. Logic HIGH enables the Snooze Mode, logic LOW disables the Snooze Mode. Do not leave floating. |
| FB | 4 | IN | Feedback Pin for the internal control loop. Connect this pin to the external feedback divider for the adjustable output versions. For the fixed output voltage versions, this pin must be left floating or connected to GND. |
| VOS | 5 | IN | Output Voltage Sense Pin for the internal control loop. Must be connected to output voltage. |
| PG | 6 | OUT | Power Good open drain output. This pin is pulled to low if the output voltage is below regulation limits. Can be left floating if not used. |
| SW | 7 | PWR | Switch Pin connected to the internal MOSFET switches and inductor terminal. Connect the inductor of the output filter here. |
| VIN | 8 | PWR | Power Supply Voltage Input. |
| Exposed Thermal Pad | — | — | Connect it to GND. The thermal pad must be soldered to achieve appropriate power dissipation and mechanical reliability. |
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage at VIN, PG, VOS(2) | –0.3 | 7 | V |
| Voltage at SW(2)(3) | –1 | 7 | V |
| Voltage at FB(2) | –0.3 | 3.6 | V |
| Voltage at EN, MODE(2) | –0.3 | VIN + 0.3 | V |
| Sink current at PG | 0 | 0.5 | mA |
| Operating junction temperature, TJ | –40 | 150 | °C |
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C |
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±500 | |||
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions(1)
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | Input voltage | 2.3 | 6 | V | |
| VOUT | Output voltage | 0.5 | 4 | V | |
| ISNOOZE | Load current in Snooze Mode | 2 | mA | ||
| TJ | Operating junction temperature | –40 | 125 | °C |
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TPS6208x | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DSG (WSON) | |||
| 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 59.7 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 70.1 | |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 30.9 | |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 1.4 | |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 31.5 | |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 8.6 | |
7.5 Electrical Characteristics
Over recommended free-air temperature range, TJ = –40°C to 125°C. Typical values are at TA = 25°C (unless otherwise noted), VIN= 3.6 V, MODE = LOW.8 Detailed Description
8.1 Overview
The TPS6208x synchronous switched mode converters are based on DCS-Control™ (Direct Control with Seamless transition into Power Save Mode). This is an advanced regulation topology that combines the advantages of hysteretic, voltage and current mode control.
The DCS-Control topology operates in pulse width modulation (PWM) mode for medium to heavy load conditions and in Power Save Mode at light load currents. In PWM mode, the converter operates with its nominal switching frequency of 2 MHz having a controlled frequency variation over the input voltage range. As the load current decreases, the converter enters Power Save Mode, reducing the switching frequency and minimizing the IC quiescent current to achieve high efficiency over the entire load current range. DCS-Control supports both operation modes (PWM and PFM) using a single building block having a seamless transition from PWM to Power Save Mode without effects on the output voltage. Fixed output voltage versions provide smallest solution size combined with lowest no load current consumption. The TPS6208x offers both excellent DC voltage and superior load transient regulation, combined with very low output voltage ripple, minimizing interference with RF circuits.
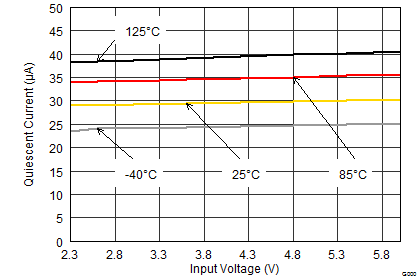
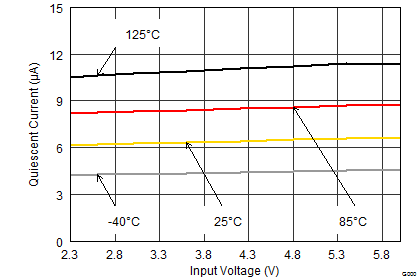
The device is equipped with Snooze Mode functionality, which is enabled with the MODE pin. Snooze Mode supports high efficiency conversion at lowest output currents below 2 mA. If no load current is drawn, the ultra low quiescent current of 6.5 µA is sufficient to maintain the output voltage. This extends battery run time by reducing the quiescent current during lowest or no load conditions in battery-driven applications. For mains-operated voltage supplies, Snooze Mode reduces the system's stand-by energy consumption. During shutdown (EN = LOW), the device reduces energy consumption to less than 1 µA.
8.2 Functional Block Diagrams
8.3 Feature Description
8.3.1 Power Good
The TPS6208x has a power good output which goes low when the output voltage is below its nominal value. The power good is high impedance once the output is above 95% of the regulated voltage, and is driven to low once the output voltage falls below typically 90% of the regulated voltage. The PG pin is an open drain output and can sink up to 0.5 mA. The power good output requires a pull-up resistor. When the device is off due to disable, UVLO or thermal shutdown, the PG pin is high impedance (see Table 1). The PG signal can be used for sequencing of multiple rails by connecting to the EN pin of other converters. Leave the PG pin unconnected when not used.
Table 1. Power Good Pin Logic Table
| Device Information | PG Logic Status | ||
| High Z | Low | ||
| Enable (EN=High) | VFB ≥ VPG | √ | |
| VFB ≤ VPG | √ | ||
| Shutdown (EN=Low) | √ | ||
| UVLO | 0.7V < VIN < VUVLO | √ | |
| Thermal Shutdown | TJ > TJSD | √ | |
| Power Supply Removal | VIN < 0.7V | √ | |
space
8.3.2 100% Duty Cycle Low Dropout Operation
The device offers low input to output voltage difference by entering 100% duty cycle mode. In this mode, the high-side MOSFET switch is constantly turned on and the low-side MOSFET is switched off. This is particularly useful in battery powered applications to achieve longest operation time by taking full advantage of the whole battery voltage range. The minimum input voltage to maintain an output voltage is calculated as:

where
- VIN,MIN = Minimum input voltage
- IOUT,MAX = Maximum output current
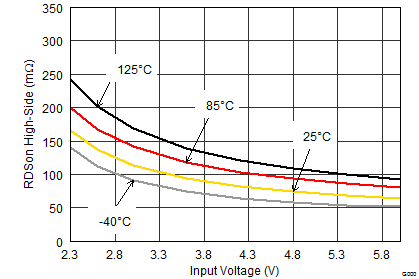
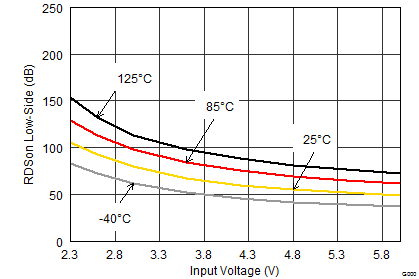
- RDS(on) = High-side FET ON-resistance
- RL = Inductor ohmic resistance
8.3.3 Output Discharge
The output gets discharged by the SW pin with a typical discharge resistor of RDIS whenever the device shuts down. This is the case when the device gets disabled by enable, thermal shutdown, or undervoltage lockout. The TPS6208A differs from the TPS62080 only in its stronger discharge.
8.3.4 Soft-Start
When EN is set to start device operation, the device starts switching after a delay of about 40 μs and VOUT rises with a slope of about 10mV/μs (See Figure 27 andFigure 29 for typical startup operation). This avoids excessive inrush current and creates a smooth output voltage rise slope. It also prevents excessive voltage drops of primary cells and rechargeable batteries with high internal impedance.
If the output voltage is not reached within the soft start time, such as in the case of heavy load, the converter enters regular operation. Consequently, the inductor current limit operates as described below. The TPS6208x is able to start into a pre-biased output capacitor. The converter starts with the applied bias voltage and ramps up the output voltage to its nominal value.
8.3.5 Undervoltage Lockout
To avoid mis-operation of the device at low input voltages, an undervoltage lockout is implemented that shuts down the device at voltages lower than VUVLO with a 120 mV typical hysteresis.
8.3.6 Thermal Shutdown
The device goes into thermal shutdown once the junction temperature exceeds typically TJSD. Once the device temperature falls below the threshold minus hysteresis, the device returns to normal operation automatically.
8.3.7 Inductor Current Limit
The Inductor Current Limit prevents the device from high inductor current and drawing excessive current from the battery or input voltage rail. Excessive current might occur with a shorted/saturated inductor or a heavy load/shorted output circuit condition.
The incorporated inductor peak current limit measures the current in the high-side and low-side power MOSFET. Once the high-side switch current limit is tripped, the high-side MOSFET is turned off and the low-side MOSFET is turned on to reduce the inductor current. When the inductor current drops down to the low-side switch current limit, the low-side MOSFET is turned off and the high-side switch is turned on again. This operation repeats until the inductor current does not reach the high-side switch current limit. Due to internal propagation delays, the real current limit value can exceed the static current limit in Electrical Characteristics.
8.4 Device Functional Modes
8.4.1 Enabling and Disabling the Device
The device is enabled by setting the EN input to a logic HIGH. Accordingly, a logic LOW disables the device. If the device is enabled, the internal power stage starts switching and regulates the output voltage to the programmed threshold. The EN input must be terminated and not left floating.
8.4.2 Power Save Mode
As the load current decreases, the TPS6208x enters Power Save Mode operation. During Power Save Mode, the converter operates with reduced switching frequency in PFM mode and with a minimum quiescent current maintaining high efficiency. Power Save Mode occurs when the inductor current becomes discontinuous. It is based on a fixed on time architecture. The typical on time is given by ton = 500 ns × (VOUT/VIN). The switching frequency over the whole load current range is shown in Figure 21 and Figure 22.
8.4.3 Snooze Mode
The TPS6208x offers a Snooze Mode function. If Snooze Mode is enabled by an external logic signal setting the MODE pin to HIGH, the device's quiescent current consumption is reduced to typically 6.5 µA. As a result, the high efficiency range is extended towards the range of lowest output currents below 2 mA. See the efficiency figures in Application Curves.
If the device is operating in Snooze Mode, a dedicated, low power consuming block monitors the output voltage. All other control blocks are snoozing during that time. If the output voltage falls below the programmed output voltage by 3.5% (typ), the control blocks wake up, regulate the output voltage and allow themselves to snooze again until the output voltage drops again. Snooze Mode operation provides a clear efficiency improvement at lowest output currents. If the load current increases, the advantage of efficiency in Snooze mode is reduced. Because the dynamic load regulation operates best if Snooze Mode is disabled, it is recommended to turn off Snooze Mode when the load current exceeds 2 mA. Generally, a microcontroller operates the MODE pin.
9 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
9.1 Application Information
The TPS62080 and TPS62080A are synchronous step-down converter whose output voltage is adjusted by component selection. The following section discusses the design of the external components to complete the power supply design for several input and output voltage options by using typical applications as a reference. The TPS62081 and TPS62082 provide a fixed output volage which do not need an external resistor divider.
9.2 Typical Application
 Figure 7. Typical Application Schematic
Figure 7. Typical Application Schematic
9.2.1 Design Requirements
For this design example, use Table 2 as the input parameters.
Table 2. Design Parameters
| DESIGN PARAMETER | EXAMPLE VALUE |
|---|---|
| Input voltage | 2.3 V to 6 V |
| Output voltage | 1.2 V |
| Output ripple voltage | < 20 mV |
| Maximum output current | 1.2 A |
9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
Table 3 lists the components used for the example.
Table 3. List of Components
| REFERENCE | DESCRIPTION | MANUFACTURER |
|---|---|---|
| C1 | 10 uF, Ceramic Capacitor, 6.3 V, X5R, size 0603 | Std |
| C2 | 22 uF, Ceramic Capacitor, 6.3 V, X5R, size 0805, GRM21BR60J226ME39L | Murata |
| L1 | 1.0 µH, Power Inductor, 2.2 A, size 3 × 3 × 1.2 mm, XFL3012-102MEB | Coilcraft |
| R1 | Depending on the output voltage of TPS62080, 1%; Not populated for TPS62081, TPS62082; | Std |
| R2 | 39.2k, Chip Resistor, 1/16W, 1%, size 0603 | Std |
| R3 | 178k, Chip Resistor, 1/16W, 1%, size 0603 | Std |
9.2.2.1 Setting the Output Voltage
The TPS608x devices are available as fixed and adjustable output voltage versions. The fixed voltage versions are internally programmed to a fixed output voltage, whereas the adjustable output voltage version needs to be programmed via an external voltage divider to set the desired output voltage.
9.2.2.1.1 Adjustable Output Voltage Version
For the adjustable output voltage version, an external resistor divider is used. By selecting R1 and R2, the output voltage is programmed to the desired value.
When the output voltage is regulated, the typical voltage at the FB pin is VFB for the adjustable devices. The following equation can be used to calculate R1 and R2.

For best accuracy, R2 should be kept smaller than 40kΩ to ensure that the current flowing through R2 is at least 100 times larger than IFB. Changing towards a lower value increases the robustness against noise injection. Changing towards higher values reduces the input current. For lowest input current during Snooze Mode, it is recommended to use a fixed output voltage version such as TPS62081 and TPS62082.
9.2.2.2 Output Filter Design
The inductor and the output capacitor together provide a low pass filter. To simplify this process, Table 4 outlines possible inductor and capacitor value combinations for most applications. Checked cells represent combinations that are proven for stability by simulation and lab test. Further combinations should be checked for each individual application.
Table 4. Matrix of Output Capacitor and Inductor Combinations
| L [µH](3) | COUT [µF](3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 22 | 47 | 100 | 150 | |
| 0.47 | |||||
| 1 | + | +(1)(2) | + | + | |
| 2.2 | + | + | + | + | |
| 4.7 | |||||
9.2.2.3 Inductor Selection
The main parameters for the inductor selection are the inductor value and then the saturation current of the inductor. To calculate the maximum inductor current under static load conditions, Equation 3 is given.

where
- IOUT,MAX = Maximum output current
- ΔIL = Inductor current ripple
- fSW = Switching frequency
- L = Inductor value
TI recommends to choose the saturation current for the inductor 20%~30% higher than the IL,MAX, out of Equation 3. A higher inductor value is also useful to lower ripple current, but increases the transient response time as well. The following inductors are recommended for use.
Table 5. List of Recommended Inductors
| INDUCTANCE [µH] |
CURRENT RATING [mA] |
DIMENSIONS L x W x H [mm3] |
DC RESISTANCE [mΩ typ] |
TYPE | MANUFACTURER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 2500 | 3 x 3 x 1.2 | 35 | XFL3012-102ME | Coilcraft |
| 1.0 | 1650 | 3 x 3 x 1.2 | 40 | LQH3NPN1R0NJ0 | Murata |
| 2.2 | 2500 | 4 x 3.7 x 1.65 | 49 | LQH44PN2R2MP0 | Murata |
| 2.2 | 1600 | 3 x 3 x 1.2 | 81 | XFL3012-222ME | Coilcraft |
9.2.2.4 Capacitor Selection
The input capacitor is the low impedance energy source for the converter which helps to provide stable operation. A low ESR multilayer ceramic capacitor is recommended for best filtering and should be placed between VIN and GND as close as possible to those pins. For most applications 10 μF is sufficient, though a larger value reduces input current ripple.
The architecture of the TPS6208X allows the use of tiny ceramic output capacitors with low equivalent series resistance (ESR). These capacitors provide low output voltage ripple and are recommended. To keep its resistance up to high frequencies and to get narrow capacitance variation with temperature, it's recommended to use X7R or X5R dielectric. The TPS6208x is designed to operate with an output capacitance of 10 µF to 100 µF and beyond, as outlined in Table 4. Load transient testing and measuring the bode plot are good ways to verify stability with larger capacitor values.
Table 6. List of Recommended Capacitors
| CAPACITANCE [µF] |
TYPE | DIMENSIONS L x W x H [mm3] |
MANUFACTURER |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | GRM188R60J106M | 0603: 1.6 x 0.8 x 0.8 | Murata |
| 22 | GRM188R60G226M | 0603: 1.6 x 0.8 x 0.8 | Murata |
| 22 | GRM21BR60J226M | 0805: 2.0 x 1.2 x 1.25 | Murata |
9.2.3 Application Curves
 Figure 8. Efficiency vs Load Current
Figure 8. Efficiency vs Load Current
 Figure 10. Efficiency vs Load Current
Figure 10. Efficiency vs Load Current
 Figure 12. Efficiency vs Load Current
Figure 12. Efficiency vs Load Current
 Figure 14. Output Voltage vs Input Voltage
Figure 14. Output Voltage vs Input Voltage
 Figure 16. Output Voltage vs Input Voltage
Figure 16. Output Voltage vs Input Voltage
 Figure 18. Output Voltage vs Load Current
Figure 18. Output Voltage vs Load Current
 Figure 20. Output Voltage vs Load Current
Figure 20. Output Voltage vs Load Current


| VIN = 3.3 V, VOUT = 1.2 V, Load Current = 10 mA |

| VIN = 3.3 V, VOUT = 1.2 V, Load Current = 50 mA to 1 A |

| VIN = 3.3 V, VOUT = 1.2 V, Load = 2.2 Ω |

| VIN = 3.3 V, VOUT = 1.2 V, No Load |
 Figure 9. Efficiency vs Load Current
Figure 9. Efficiency vs Load Current
 Figure 11. Efficiency vs Load Current
Figure 11. Efficiency vs Load Current
 Figure 13. Output Voltage vs Input Voltage
Figure 13. Output Voltage vs Input Voltage
 Figure 15. Output Voltage vs Input Voltage
Figure 15. Output Voltage vs Input Voltage
 Figure 17. Output Voltage vs Load Current
Figure 17. Output Voltage vs Load Current
 Figure 19. Output Voltage vs Load Current
Figure 19. Output Voltage vs Load Current
 Figure 21. Switching Frequency vs Load Current
Figure 21. Switching Frequency vs Load Current

| VIN = 3.3 V, VOUT = 1.2 V, Load Current = 500 mA |

| VIN = 3.3 V, VOUT = 1.2 V, Load Current = 2 mA |

| VIN = 3.3 V to 4.2 V, VOUT = 1.2 V, Load = 2.2 Ω |

| VIN = 3.3 V, VOUT = 1.2 V, No Load |
10 Power Supply Recommendations
The device is designed to operate from an input supply voltage range between 2.3 V and 6 V. Ensure that the input power supply has a sufficient current rating for the application.
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
The PCB layout is an important step to maintain the high performance of the TPS6208x devices.
The input/output capacitors and the inductor should be placed as close as possible to the IC. This keeps the traces short. Routing these traces direct and wide results in low trace resistance and low parasitic inductance. A common power GND should be used. The low-side of the input and output capacitors must be connected properly to the power GND to avoid a GND potential shift.
The sense traces connected to the FB and VOS pins are signal traces. Special care should be taken to avoid noise being induced. By a direct routing, parasitic inductance can be kept small. GND layers might be used for shielding. Keep these traces away from SW nodes.
11.2 Layout Example
space
 Figure 31. PCB Layout Suggestion
Figure 31. PCB Layout Suggestion
11.3 Thermal Considerations
Implementation of integrated circuits in low-profile and fine-pitch surface-mount packages typically requires special attention to power dissipation. Many system-dependent issues such as thermal coupling, airflow, added heat sinks and convection surfaces, and the presence of other heat-generating components affect the power-dissipation limits of a given component.
Three basic approaches for enhancing thermal performance are listed below:
- Improving the power dissipation capability of the PCB design
- Improving the thermal coupling of the component to the PCB by soldering Exposed Thermal Pad
- Introducing airflow in the system
For more details on how to use the thermal parameters, see the application notes: Thermal Characteristics of Linear and Logic Packages Using JEDEC PCB Designs (SZZA017) and Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics (SPRA953).