SLAAEI3 February 2024 MSPM0C1103 , MSPM0C1103-Q1 , MSPM0C1104 , MSPM0C1104-Q1 , MSPM0G1105 , MSPM0G1106 , MSPM0G1107 , MSPM0G1505 , MSPM0G1506 , MSPM0G1507 , MSPM0G1519 , MSPM0G3105 , MSPM0G3105-Q1 , MSPM0G3106 , MSPM0G3106-Q1 , MSPM0G3107 , MSPM0G3107-Q1 , MSPM0G3505 , MSPM0G3505-Q1 , MSPM0G3506 , MSPM0G3506-Q1 , MSPM0G3507 , MSPM0G3507-Q1 , MSPM0G3519 , MSPM0L1105 , MSPM0L1106 , MSPM0L1117 , MSPM0L1227 , MSPM0L1227-Q1 , MSPM0L1228 , MSPM0L1228-Q1 , MSPM0L1303 , MSPM0L1304 , MSPM0L1304-Q1 , MSPM0L1305 , MSPM0L1305-Q1 , MSPM0L1306 , MSPM0L1306-Q1 , MSPM0L1343 , MSPM0L1344 , MSPM0L1345 , MSPM0L1346 , MSPM0L2227 , MSPM0L2227-Q1 , MSPM0L2228 , MSPM0L2228-Q1
3 Derivation of Formulas
First of all, the premise of the formula is that the operating current of the MCU is consistent at different operating voltages. So the operating current at different voltages was tested. The starting voltage was 3.3V, and the supply voltage was gradually reduced, during which the change in operating current was measured by the ammeter connected in series between the power supply and the MCU. Here comes the result. Figure 3-1 shows that the current remains the same while MCU is working normally (VCC is greater than 1.6V). Besides, the device operates in run0, sleep0, and stop0 modes with currents of 1.55mA, 0.93mA, and 0.32mA, respectively, which conform to the device-specific data sheet specifications.
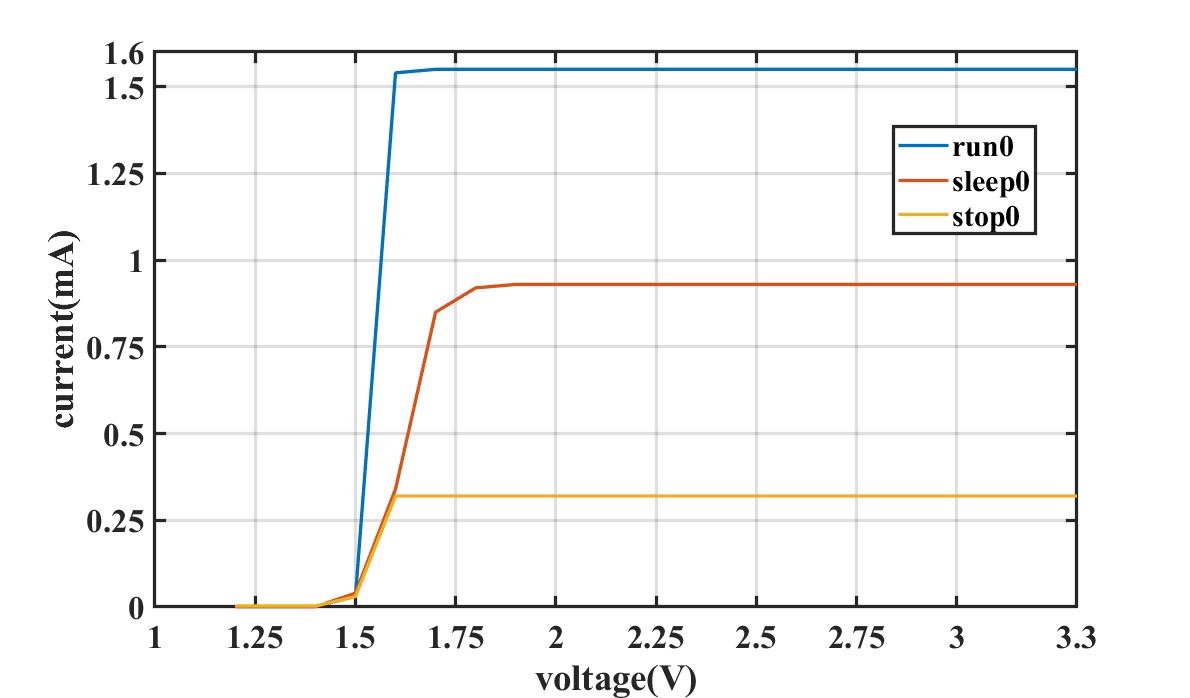 Figure 3-1 Diagram of the Operating Current of the
MCU vs. Supply Voltage
Figure 3-1 Diagram of the Operating Current of the
MCU vs. Supply VoltageBased on constant current, the MCU maintains the required energy for:
And from a capacitance point of view, the reduced energy can be expressed as:
The energy of the capacitor is used to supply the normal operation of the MCU, so Equation 2 and Equation 3 can be connected to further obtain the equipment operating maintenance time t which is expressed as Equation 2.