SLLA486B May 2020 – October 2024 ISO1042 , ISO1042-Q1 , ISO1044 , ISO1050 , ISOW1044
- 1
- Top Design Questions About Isolated CAN Bus Design
- Trademarks
- 1 When Do I Need to Isolate CAN?
- 2 What are the Options Available to Isolate CAN Bus?
- 3 Now That I Have Isolated CAN Signal Path, How Do I Generate Isolated Power?
- 4 What’s the Reason Behind Terminating the Bus, Do I Need it, and How to Achieve it?
- 5 What’s the Difference Between Common Mode Range and Bus Standoff Mentioned in Data Sheet?
- 6 Now That I Have Taken Care of the Termination Resistor, What Other Components do I Need on the Bus Side?
- 7 When Connecting Isolated CAN Nodes in a Network, What Should be Done with the Floating Bus-Side Ground Connection?
- 8 Is There a Limitation on Minimum Data Rate That I Can Operate? What About the Maximum Data Rate Achievable in a Network?
- 9 Is There a Limit on Maximum Number of Nodes That I Can Connect in CAN Network?
- 10What Factors Decide the Maximum Communication Distance in a CAN Network?
- 11What is the Maximum Value of Bus Capacitance That Can be Introduced Between CANH to GND and CANL to GND? Can Higher Capacitance Damage the Device?
- 12Is There a Way to Extend the Maximum Communication Distance?
- 13What is Stub Length? What are the Design Considerations Around it?
- 14I am Seeing Larger Differential CAN Voltage for Some Bits of CAN Packet Compared to Rest of the Packet When I am Communicating in a Network with Multiple Nodes Connected. Why?
- 15References
- 16Revision History
14 I am Seeing Larger Differential CAN Voltage for Some Bits of CAN Packet Compared to Rest of the Packet When I am Communicating in a Network with Multiple Nodes Connected. Why?
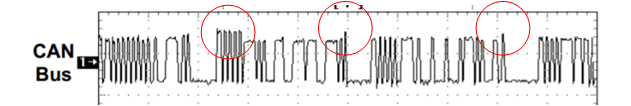 Figure 14-1 Differential CAN Bus Voltage Showing Higher
Voltage on Some Bits
Figure 14-1 Differential CAN Bus Voltage Showing Higher
Voltage on Some BitsThe CAN packet (shown in Figure 14-2) is made up of ID bits at the start of packet which are used for bitwise arbitration to determine the priority over which node will continue transmission and which other node(s) will stop. Also, towards the end of packet, ACK is acknowledgment bit which is driven dominant by all nodes which correctly receive the packet. So when multiple nodes on bus drive dominant at the same time, the differential voltage is higher in amplitude as opposed to other bits which are just driven by master transmitter node. Figure 14-3 shows a snapshot of CAN bus traffic with three nodes communicating, where we can clearly see larger voltage magnitude on CAN bus. These time instances are during acknowledgment bit or when B and C are transmitting together during ID phase.
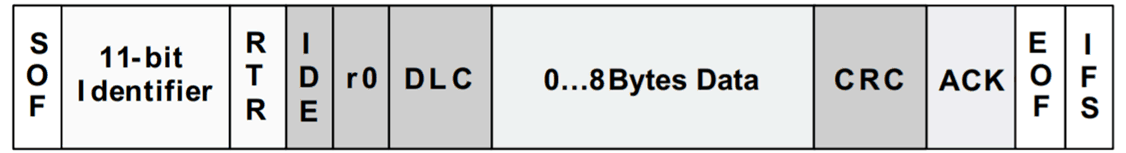 Figure 14-2 CAN Packet: See ID Bits at Start of the Frame
and ACK Near End of the Frame
Figure 14-2 CAN Packet: See ID Bits at Start of the Frame
and ACK Near End of the Frame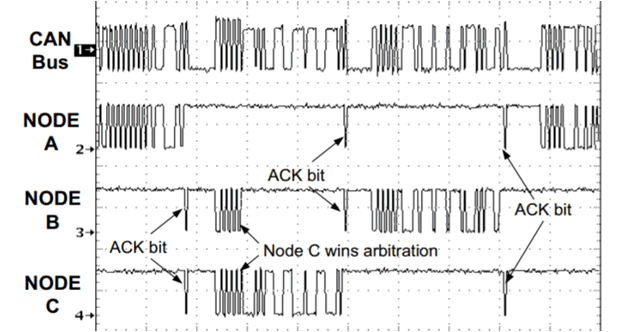 Figure 14-3 CAN Bus Waveforms Describing Why Some Bits are
Larger in Magnitude
Figure 14-3 CAN Bus Waveforms Describing Why Some Bits are
Larger in Magnitude