SLLA639 May 2024 THVD1419 , THVD1429 , THVD1439 , THVD1449 , THVD2419 , THVD2429
4 THVD24x9x – The Next Generation of Integrated Surge Protected RS-485 Devices from TI
Until recently the trade-offs between integrated and discrete protection was straight forward. Discrete designs offer more flexibility in the design at the cost of a higher design complexity, while integrated designs offered a simpler and smaller design with at the cost of a narrower design scope and the premium paid for the integration. To combat the issue of the narrower scope on the previous generation of surge protected RS-485 Transceivers, TI’s new THVD24x9x family increases the flexibility of applications that can be supported by raising both the stand-off voltage range as well as the common mode voltage range.
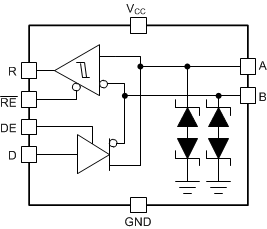 Figure 4-1 THVD24X9 Family of Devices
Functional Block Diagram
Figure 4-1 THVD24X9 Family of Devices
Functional Block Diagram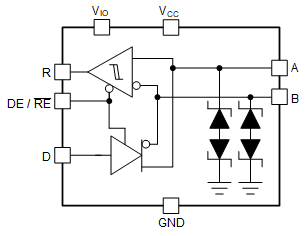 Figure 4-2 THVD24X9V Family of
Devices Functional Block Diagram in SOIC Package
Figure 4-2 THVD24X9V Family of
Devices Functional Block Diagram in SOIC PackageThe next generation in surge protected RS-485 from TI offers multiple benefits above the last generation of integrated surge. These can be broken down into three main categories: standard RS-485 operation, design size, and controller interface.
When looking at standard RS-485 operation the THVD24x9x family, including devices like THVD2419 and THVD2429, offers extended common mode voltage ratings of up to ±25V as well as stand-off voltages of up to +/-42V in addition to their IEC 61000 4-5 ratings (±2.5kV for SOIC packages and ±1.5kV for VSON packages). This allows an integrated surge protected device in systems where large ground potential differences are likely – this is especially important in systems where the transceiver is connected to a motor as during operation systems with a motor can put a large amount of current on the ground line. In systems with large ground lines this can create large voltage drops on the reference plane between nodes. Standard RS-485 expects this to some degree – but in some industrial systems the standard level isn’t enough. In the past this can mean picking a different transceiver that supports higher common mode and placing a discrete protection design in front – but the THVD24x9x family of devices prevents this requirement by allowing a large common voltage range during normal operation.
Another benefit of the THVD24x9x family of device is that beyond the standard 8-pin SOIC package it also has offerings in the smaller 10-pin VSON package which only takes up 9mm^2 of area. Not only does the designer get the size reduction in a standard SOIC package, but they can use the VSON package and only use 9mm^2 of board space for the simplest form of surge protection. Using the discrete example from section one, the diode plus pulse proof resistors takes up more space, 9.3mm^2 than one of the VSON offerings from the THVD24x9x family of devices. This means a classic discrete implementation has the protection circuit bigger than the THVD24x9x in a VSON package which not only gives the integrated protection, but also gives the transceiver as well in a tiny 3mm x 3mm package.
Finally, another major benefit is the devices in the THVD24x9x that take the form THVD24x9V have an additional supply pin that can allow a separate voltage supply for the RS-485 bus as well as a separate supply for the logic pins. This separate supply pin can be powered as low as 1.65V allowing a 1.8V controller to control the RS-485 node. Without the separate supply pin an additional level translation circuit can be introduced. Not only does the THVD24x9V line of devices integrate protection, but also integrates level translation allowing for a much more flexible use RS-485 device that also protects in the case of surge transients.