SLAAE75A November 2022 – March 2023 MSPM0L1105 , MSPM0L1106 , MSPM0L1227 , MSPM0L1228 , MSPM0L1228-Q1 , MSPM0L1303 , MSPM0L1304 , MSPM0L1304-Q1 , MSPM0L1305 , MSPM0L1305-Q1 , MSPM0L1306 , MSPM0L1306-Q1 , MSPM0L1343 , MSPM0L1344 , MSPM0L1345 , MSPM0L1346 , MSPM0L2227 , MSPM0L2228 , MSPM0L2228-Q1
4.1 Internal Oscillators
Internal Low-Frequency Oscillator (LFOSC)
LFOSC is an on-chip low power oscillator that is factory trimmed to a frequency of 32.768 kHz. It provides a low-frequency clock that can be used to help the system achieve low-power. LFOSC can provide higher accuracy when used over a reduced temperature range. See the device-specific data sheet for details.
 Figure 4-1 MSPM0L Series LFOSC
Figure 4-1 MSPM0L Series LFOSCInternal System Oscillator (SYSOSC)
SYSOSC is an on-chip, accurate, and configurable oscillator with factory-trimmed frequencies of 32 MHz (base frequency) and 4 MHz (low frequency), as well as support for user-trimmed operation at either 24 MHz or 16 MHz. It provides a high-frequency clock that lets the CPU run at high speed for executing code and processing performance.
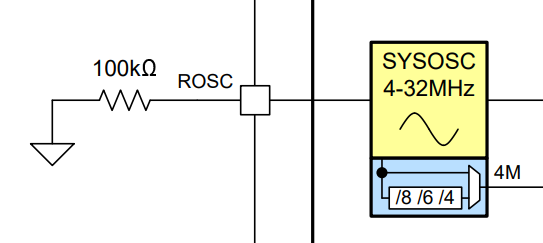 Figure 4-2 MSPM0L Series SYSOSC
Figure 4-2 MSPM0L Series SYSOSCSYSOSC Frequency Correction Loop
The additional hardware setting for this oscillator is an external resistor, populated between the ROSC pin and VSS, to increase SYSOSC from a base accuracy of ±2.5% across temperature.
The overall SYSOSC application accuracy is determined by combining the following error sources to determine the total error:
- The ROSC reference resistor error (due to tolerance and temperature drift)
- The SYSOSC circuit error in FCL mode (±0.75% for -40°C to 85°C or ±0.90% for -40°C to 125°C)
#GUID-A8A7C48C-A7E1-460B-9687-642B5C2DEB96/GUID-F6EEBED2-F653-4C16-A93E-B1BFC9DF65CB shows how to calculate the SYSOSC application accuracy for two different ROSC resistor specs across two temperature ranges. For more details, refer to the MSPM0 L-Series 32-MHz Microcontrollers Technical Reference Manual.
| Ambient Temperature (TA) | -40 ≤ TA ≤ 125°C | -40 ≤ TA ≤ 85°C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROSC Resistor Parameters | ±0.1% 25 ppm/°C | ±0.5% 25 ppm/°C | ±0.1% 25 ppm/°C | ±0.5% 25 ppm/°C |
| Nominal ROSC resistance (ROSCnom) | 100 kΩ | |||
| Maximum ROSC resistance (at 25°C) | 100.1 kΩ | 100.5 kΩ | 100.1 kΩ | 100.5 kΩ |
| Minimum ROSC resistance (at 25°C) | 99.9 kΩ | 99.5 kΩ | 99.9 kΩ | 99.5 kΩ |
| ROSC resistor TCR | 25 ppm/°C | |||
| ROSC temperature drift | -0.16% to 0.25% | -0.16% to 0.15% | ||
| Maximum ROSC resistance (at high temperature) (ROSCmax) | 100.35 kΩ | 100.75 kΩ | 100.25 kΩ | 100.65 kΩ |
| Minimum ROSC resistance (at low temperature) (ROSCmin) | 99.74 kΩ | 99.34 kΩ | 99.74 kΩ | 99.34 kΩ |
| ROSC resistance error (high temperature) (ROSCerr+) | +0.35% | +0.75% | + 0.25% | +0.65% |
| ROSC resistance error (low temperature) (ROSCerr-) | -0.26% | -0.66% | -0.26% | -0.66% |
| SYSOSC circuit error (SYSOSCerr) | ±0.9% | ±0.75% | ||
| Total accuracy (TOTerr-, TOTerr+) | -1.2% to +1.3% | -1.6% to +1.7% | -1.0% to +1.0% | -1.4% to +1.4% |