SLAAED1D June 2023 – October 2024 MSPM0C1103 , MSPM0C1103-Q1 , MSPM0C1104 , MSPM0C1104-Q1 , MSPM0G1107 , MSPM0G1505 , MSPM0G1506 , MSPM0G1507 , MSPM0G1519 , MSPM0G3105 , MSPM0G3105-Q1 , MSPM0G3106 , MSPM0G3106-Q1 , MSPM0G3107 , MSPM0G3107-Q1 , MSPM0G3505 , MSPM0G3505-Q1 , MSPM0G3506 , MSPM0G3506-Q1 , MSPM0G3507 , MSPM0G3507-Q1 , MSPM0G3519 , MSPM0L1105 , MSPM0L1106 , MSPM0L1117 , MSPM0L1227 , MSPM0L1228 , MSPM0L1228-Q1 , MSPM0L1303 , MSPM0L1304 , MSPM0L1304-Q1 , MSPM0L1305 , MSPM0L1305-Q1 , MSPM0L1306 , MSPM0L1306-Q1 , MSPM0L1343 , MSPM0L1344 , MSPM0L1345 , MSPM0L1346 , MSPM0L2227 , MSPM0L2228 , MSPM0L2228-Q1
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Overview
- 2Step 1: MSPM0 Selection
- 3Step 2: MSPM0 Evaluation
- 4Step 3: Hardware Design
- 5Step 4: Mass Production
- 6Step 5: Quality and Reliability Instructions
- 7Common Questions
- 8Additional Information
- 9Summary
- Revision History
3.3.2.1 Basic Concept
This section introduces SysConfig function blocks and basic operation.
As shown in Figure 3-9, the basic view is shown after SysConfig is opened. SysConfig has two function blocks: the peripheral usage block, which is used to show the added peripherals and the peripheral setting menu entrance. Second is the peripheral setting, which is used to configure the MCU peripherals.
After clicking the buttons on the right side of the screen, the user can open more windows. Generated files are shown after the project build. The user can click the files individually to know the changes after doing new settings on SysConfig. The MCU view is used to view the pin assignment and pin resources, which is also an entrance for MSPM0 migration.
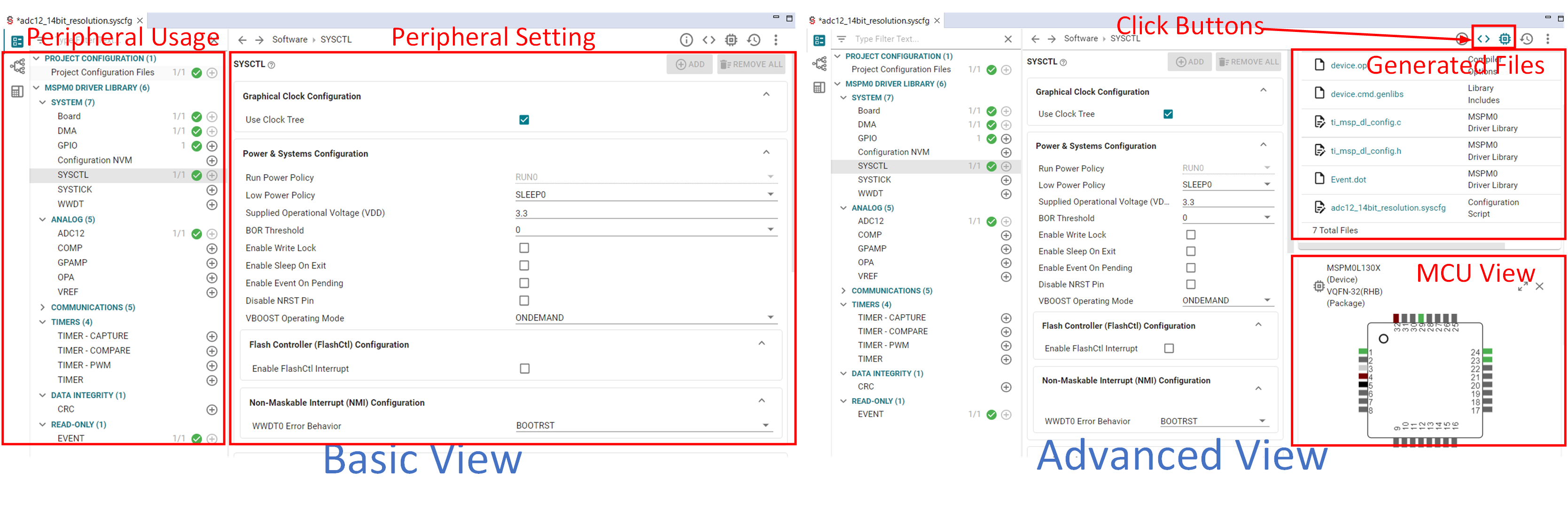 Figure 3-9 SysConfig View
Figure 3-9 SysConfig ViewThe basic operations of SysConfig, includes adding peripherals, removing peripherals and referring the peripheral or function descriptions. As SysConfig is a low level MSPM0 peripheral setting GUI, see the technical reference manual or the peripheral examples to obtain a better understanding.
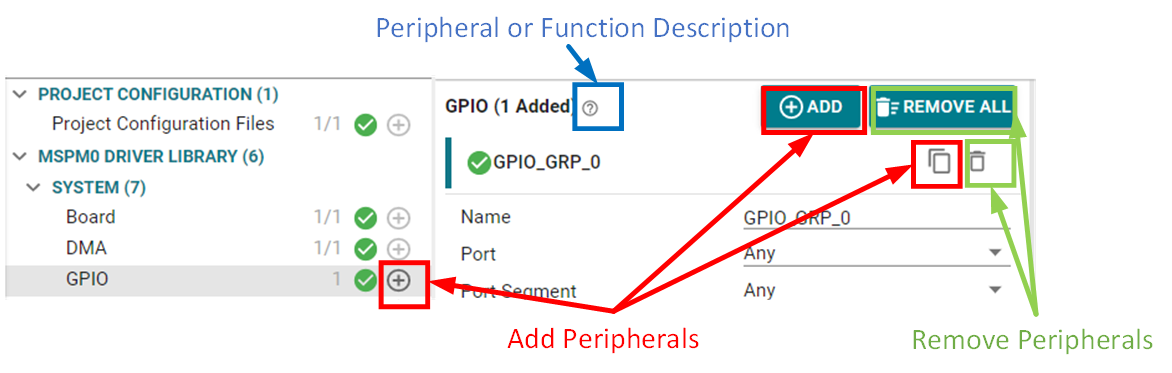 Figure 3-10 Basic Operations
Figure 3-10 Basic Operations