SLAAED1D June 2023 – October 2024 MSPM0C1103 , MSPM0C1103-Q1 , MSPM0C1104 , MSPM0C1104-Q1 , MSPM0G1107 , MSPM0G1505 , MSPM0G1506 , MSPM0G1507 , MSPM0G1519 , MSPM0G3105 , MSPM0G3105-Q1 , MSPM0G3106 , MSPM0G3106-Q1 , MSPM0G3107 , MSPM0G3107-Q1 , MSPM0G3505 , MSPM0G3505-Q1 , MSPM0G3506 , MSPM0G3506-Q1 , MSPM0G3507 , MSPM0G3507-Q1 , MSPM0G3519 , MSPM0L1105 , MSPM0L1106 , MSPM0L1117 , MSPM0L1227 , MSPM0L1228 , MSPM0L1228-Q1 , MSPM0L1303 , MSPM0L1304 , MSPM0L1304-Q1 , MSPM0L1305 , MSPM0L1305-Q1 , MSPM0L1306 , MSPM0L1306-Q1 , MSPM0L1343 , MSPM0L1344 , MSPM0L1345 , MSPM0L1346 , MSPM0L2227 , MSPM0L2228 , MSPM0L2228-Q1
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Overview
- 2Step 1: MSPM0 Selection
- 3Step 2: MSPM0 Evaluation
- 4Step 3: Hardware Design
- 5Step 4: Mass Production
- 6Step 5: Quality and Reliability Instructions
- 7Common Questions
- 8Additional Information
- 9Summary
- Revision History
3.4.1.3 Import a SDK Example
Open CCS. The workspace is the address to copy an imported project to.
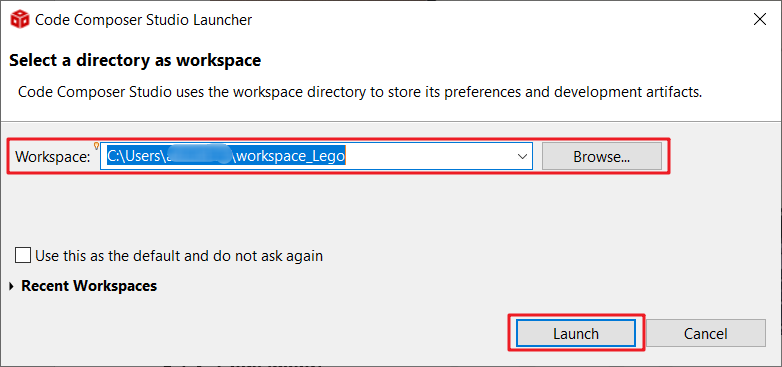 Figure 3-21 Select CCS Workspace
Figure 3-21 Select CCS WorkspaceImport an example with the TI-Clang compiler from the installed SDK.
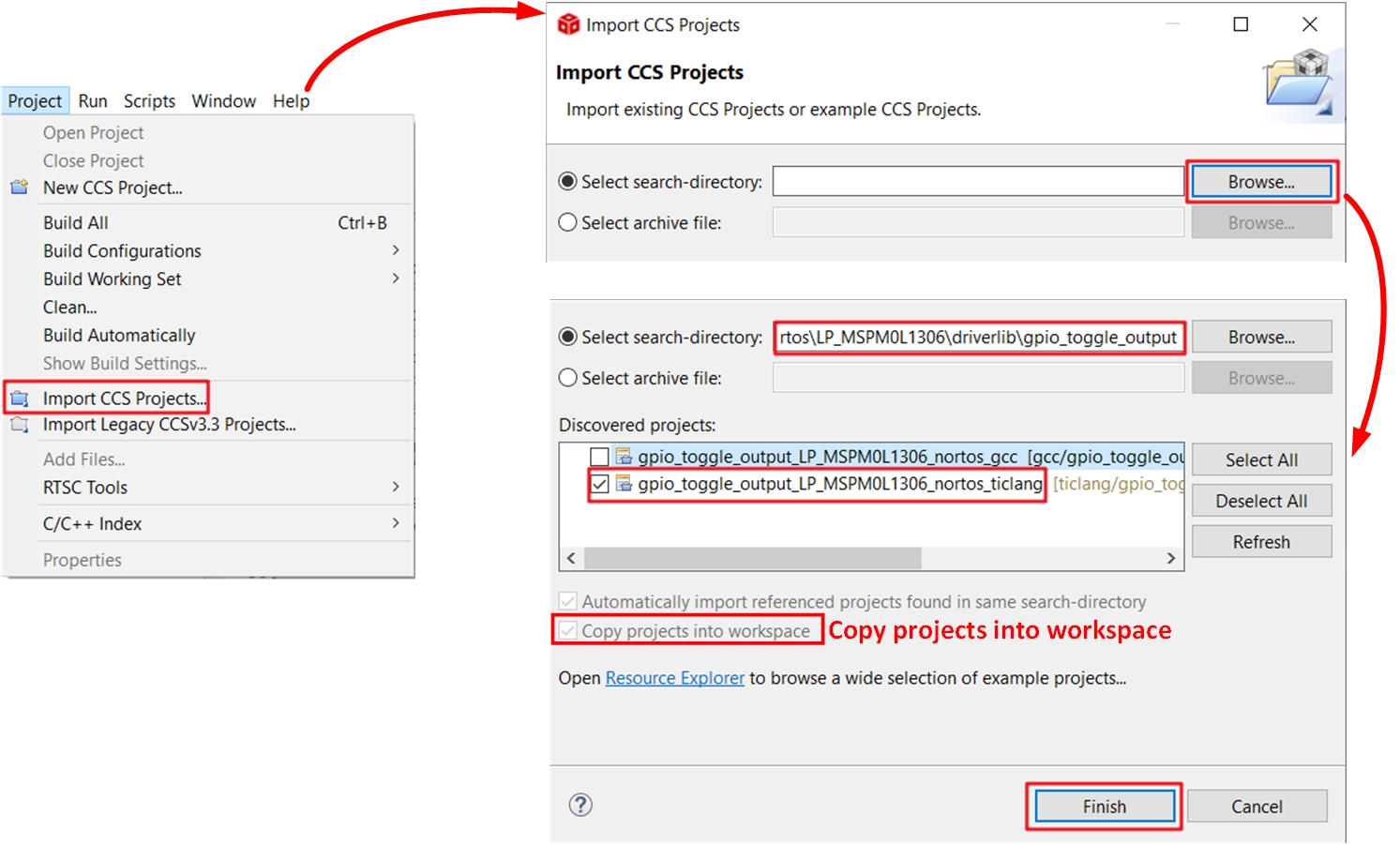 Figure 3-22 Import Project
Figure 3-22 Import ProjectHere is the view of the imported project. The most important files are in red. This section shows a brief introduction.
- Sysconfig generated code: Click the Build button, the SysConfig generates the code under the Debug\syscfg folder.
- .map file: In the Debug folder, refer to the .map file to find out more about the memory usage condition.
- Main function .c file: Includes the main function in the file.
- .cmd file: Define the MCU memory allocation. In the latest CCS, the user can select to allow SysConfig to generate the allocation automatically.
- SysConfig: GUI tool to generate the peripheral setting code.
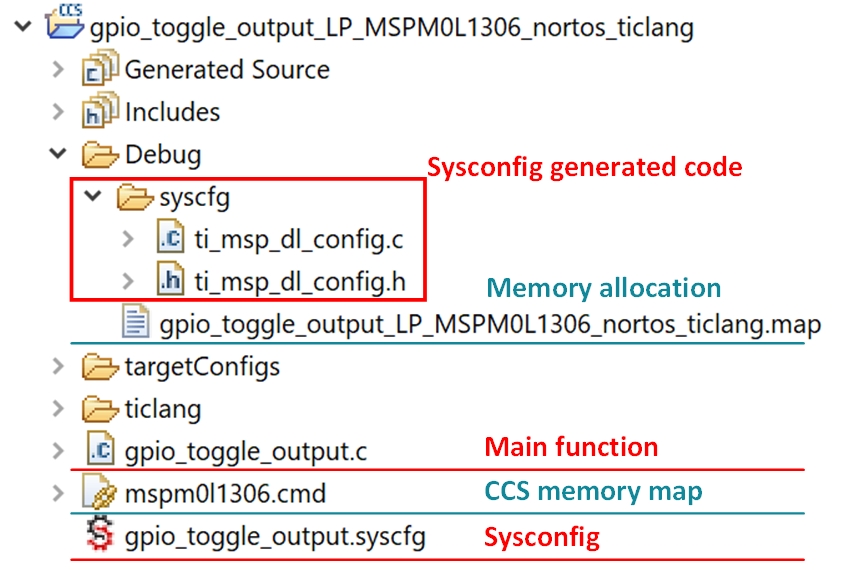 Figure 3-23 CCS Project Overview
Figure 3-23 CCS Project Overview