SLAAED1D June 2023 – October 2024 MSPM0C1103 , MSPM0C1103-Q1 , MSPM0C1104 , MSPM0C1104-Q1 , MSPM0G1107 , MSPM0G1505 , MSPM0G1506 , MSPM0G1507 , MSPM0G1519 , MSPM0G3105 , MSPM0G3105-Q1 , MSPM0G3106 , MSPM0G3106-Q1 , MSPM0G3107 , MSPM0G3107-Q1 , MSPM0G3505 , MSPM0G3505-Q1 , MSPM0G3506 , MSPM0G3506-Q1 , MSPM0G3507 , MSPM0G3507-Q1 , MSPM0G3519 , MSPM0L1105 , MSPM0L1106 , MSPM0L1227 , MSPM0L1228 , MSPM0L1228-Q1 , MSPM0L1303 , MSPM0L1304 , MSPM0L1304-Q1 , MSPM0L1305 , MSPM0L1305-Q1 , MSPM0L1306 , MSPM0L1306-Q1 , MSPM0L1343 , MSPM0L1344 , MSPM0L1345 , MSPM0L1346 , MSPM0L2227 , MSPM0L2228 , MSPM0L2228-Q1
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Overview
- 2Step 1: MSPM0 Selection
- 3Step 2: MSPM0 Evaluation
- 4Step 3: Hardware Design
- 5Step 4: Mass Production
- 6Step 5: Quality and Reliability Instructions
- 7Common Questions
- 8Additional Information
- 9Summary
- Revision History
3.4.1.5 Migrating Between MSPM0 Derivatives
Project migration in this scope means updating relevant project configuration files and settings that are specific to the derivative, including linker files, startup files, and included libraries. To facilitate project migration, SysConfig generates project configuration files by default, which can be controlled through the project configuration module.
Here are the migration steps based on CCS:
- In SysConfig, enable the device view and click on SWITCH.
- Select New Values for the Device, Package, and CCS Launch Device to migrate the project configuration to a new device, and then click CONFIRM.
- After confirming the new device values, SysConfig highlights an error on the project configuration module. The user must select the new device in the Select Device options. Make sure the device selection matches what was selected for CCS Launch Device in the previous step.
- Note that SysConfig highlights any conflicts with the migration, such as unavailable pins and peripherals. Fix any conflicts as needed, and save all the changes to the SysConfig configuration script. Migration is now complete and the user can build a project for the new target device.
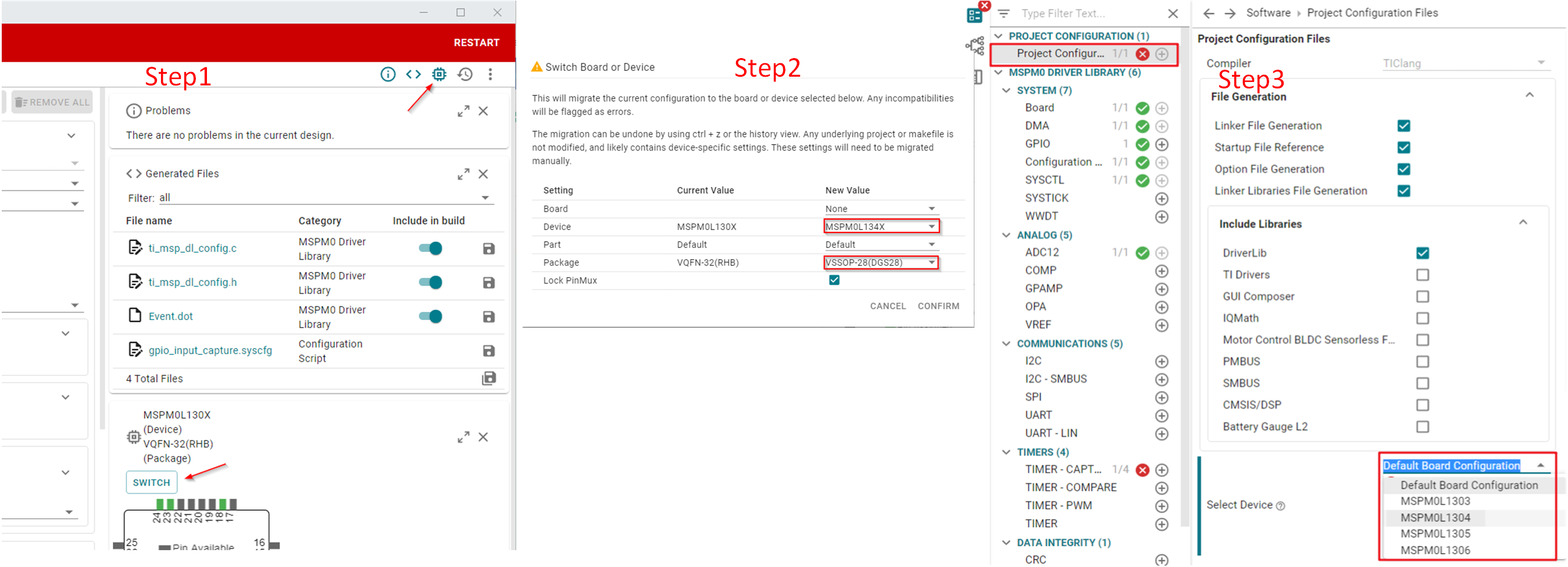 Figure 3-27 Migrating Between MSPM0 Derivatives
Figure 3-27 Migrating Between MSPM0 Derivatives