SLUA475 November 2016 BQ2060A , BQ20Z80 , BQ40Z50-R1 , BQ40Z50-R2 , BQ40Z60 , BQ78350-R1 , BQ78350-R1A
1.2.4.2 Example 2
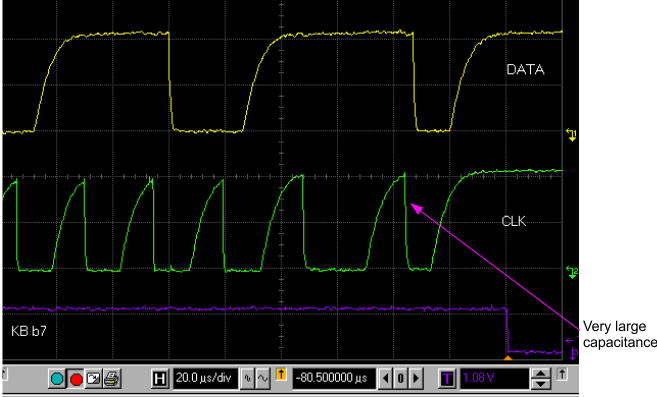 Figure 7. Example 2
Figure 7. Example 2 The problem associated with Example 2 (shown in Figure 7) was a matter of receiving incorrect data. Although almost every bit received was correct, an incorrect bit was occasionally received. As pointed out in Figure 7, a large capacitance on the line sometimes caused a 1 to be read as a 0 because the data line was just on the edge of going up fast enough to be a 1 by the time the clock went to a 1. In Example 2 protection diodes were used on the bus that had a very high capacitance. By removing the high-capacitance protection diodes and using a more common protection circuitry as shown in Figure 8, the problem was solved.
 Figure 8. Common Protection Circuitry
Figure 8. Common Protection Circuitry