SLUAAY2 December 2024 ISO5451 , ISO5451-Q1 , ISO5452 , ISO5452-Q1 , ISO5851 , ISO5851-Q1 , ISO5852S , ISO5852S-EP , ISO5852S-Q1 , UCC21710 , UCC21710-Q1 , UCC21717-Q1 , UCC21732 , UCC21732-Q1 , UCC21736-Q1 , UCC21737-Q1 , UCC21738-Q1 , UCC21739-Q1 , UCC21750 , UCC21750-Q1 , UCC21755-Q1 , UCC21756-Q1 , UCC21759-Q1
5.1 DESAT Circuit Component Selection
To achieve proper short circuit and overcurrent detection, it is crucial to choose the right components for the DESAT circuitry. The DESAT circuitry usually includes a blanking capacitor (CBLK), a current-limiting resistor (RLIM), and high-voltage diode(s) (DHV(1,2..)). Depending on system conditions, usually protection diodes (DD1, DD2) and a zener diode in the DESAT path (DZ) are also used.
During normal operation of the power switch, the VDS or VCE is lower than the desired VDS/VCE threshold. Under this condition, the high-voltage diodes are forward biased, and the DESAT pin internal charging current (ICHG) flows through the high-voltage diodes into the collector or drain of the power switch. Thus, voltage on the DESAT pin is lower than the DESAT detection threshold, and DESAT is not triggered.
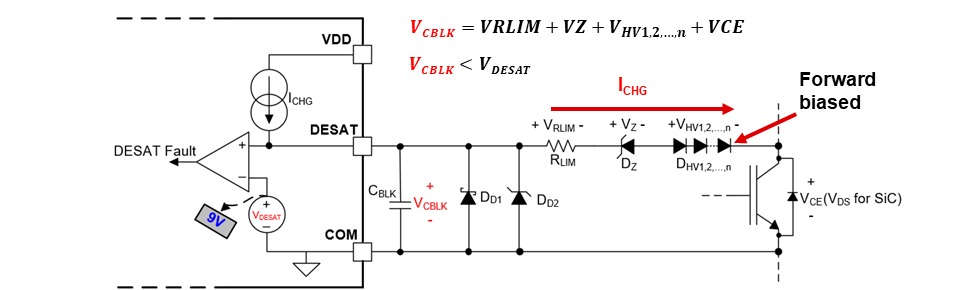 Figure 5-1 DESAT Normal Operation
Figure 5-1 DESAT Normal OperationDuring a short-circuit or overcurrent event, the VDS or VCE is higher than the desired VDS/VCE threshold. Under this condition, the high-voltage diodes become reverse biased, and the DESAT pin internal charging current cannot flow through the diodes. As a result, ICHG starts charging the blanking capacitor, causing the voltage on the DESAT pin to rapidly rise up to above the DESAT detection threshold. After a deglitch period, DESAT is triggered in this case.
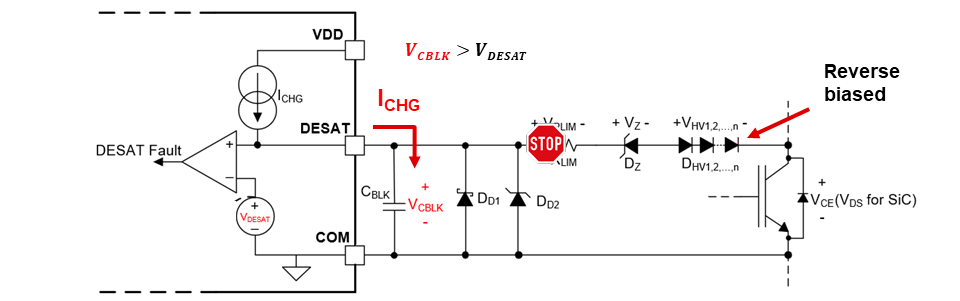 Figure 5-2 DESAT Short-Circuit Operation
Figure 5-2 DESAT Short-Circuit OperationTo correctly select the external circuitry values, first determine the VDS/VCE threshold above, which the system is considered short-circuited or overcurrent. Then, design the external circuitry values using Equation 1:
During normal operation:
During short-circuit or overcurrent operation:
Besides the voltage detection threshold, also pay attention to the blanking capacitor charging time (tBLK), since it contributes to the total DESAT detection and shutdown time. tBLK can be estimated using Equation 3:
Where Cblk is the size of the blanking capacitor, Vdesat is the DESAT detection threshold, and ICHG is the DESAT charging current.
After taking all elements into consideration, the total DESAT detection time can be calculated by using Equation 4:
Where tDESATLEB is the leading edge blanking time, tBLK is the blanking capacitor charging time, and tDESATFIL is the DESAT filter time.