SLUAAY2 December 2024 ISO5451 , ISO5451-Q1 , ISO5452 , ISO5452-Q1 , ISO5851 , ISO5851-Q1 , ISO5852S , ISO5852S-EP , ISO5852S-Q1 , UCC21710 , UCC21710-Q1 , UCC21717-Q1 , UCC21732 , UCC21732-Q1 , UCC21736-Q1 , UCC21737-Q1 , UCC21738-Q1 , UCC21739-Q1 , UCC21750 , UCC21750-Q1 , UCC21755-Q1 , UCC21756-Q1 , UCC21759-Q1
5.2 Effect of Parasitic Elements
Besides the values of DESAT external circuitry (capacitance, resistance, forward voltage drop, and so forth), it is also important to pay attention to the parasitics introduced by the external circuitry and the effects. Two parasitic elements that can affect DESAT detection time are discussed here: the junction capacitance of the high-voltage diode and the parasitic capacitance on the DESAT node.
The junction capacitance of the high-voltage diode can affect DESAT detection time, because it can couple dV/dt from the drain/collector and causing current flow. When there is a negative dV/dt on the drain/collector, current is pulled from the DESAT pin; when there is a positive dV/dt on the drain/collector, current is injected into the DESAT pin. The delta current can either increase or decrease DESAT detection time.Figure 5-3 shows how larger high-voltage diode junction capacitance can result in larger DESAT pin voltage dip, resulting in longer blanking capacitor charging time.
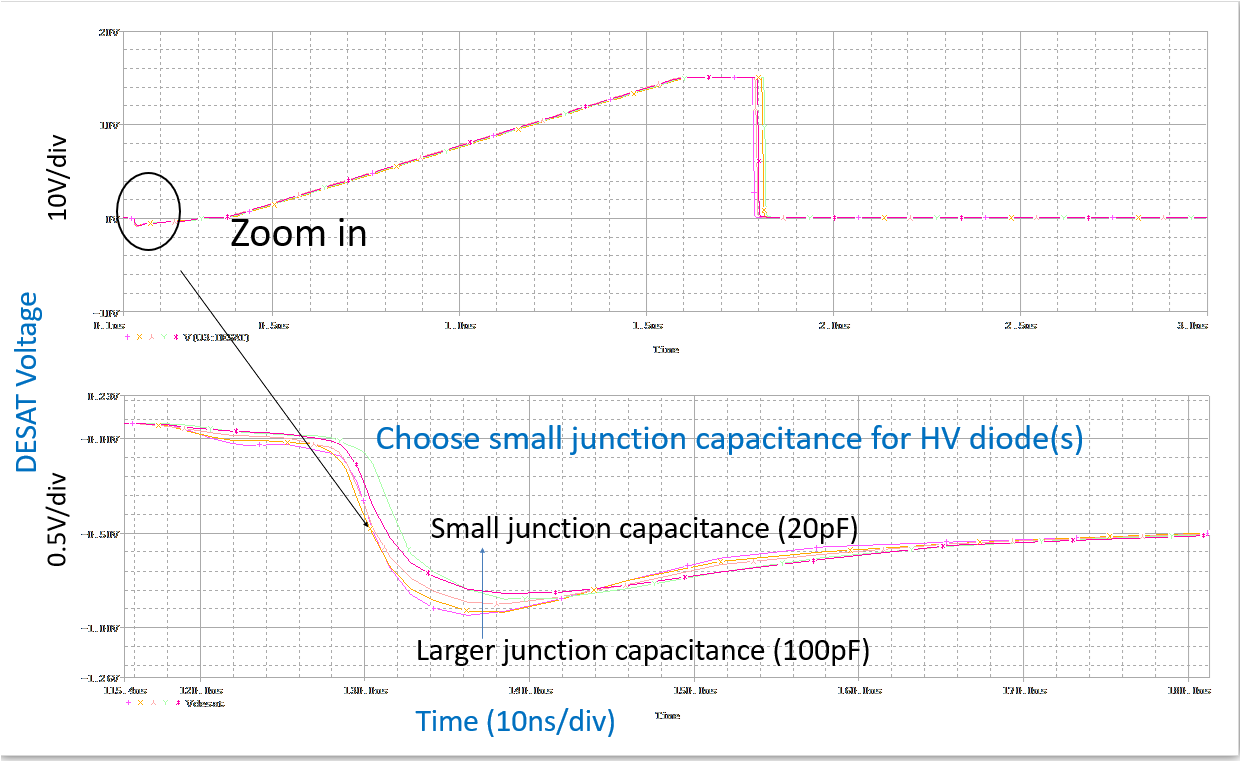 Figure 5-3 Junction Capacitance
Simulation Result
Figure 5-3 Junction Capacitance
Simulation ResultAdditional parasitic capacitance on the DESAT node can also affect DESAT detection time. These parasitic capacitance can come from either the clamping diodes on DESAT (Schottky diode and/or Zener diode) or the PCB trace capacitance. The clamping diode's junction capacitance is usually around 5pF, while the PCB trace parasitic capacitance varies by the system, usually in the 5pF-20pF range. Take the extra capacitance value into consideration when calculating DESAT blanking capacitor charge time.