SSZTCD6 august 2015 TPS40400 , TPS40422 , TPS40425 , TPS40428 , TPS53647 , TPS53819A , TPS53915 , TPS544B20 , TPS544B25 , TPS544C20 , TPS544C25
Do you need to monitor system operation or collect data about the power supply? If the answer is yes, then PMBus is for you.
PMBus is an industry-standard protocol that facilitates 2-wire digital communication with power converters and other devices in a power system. Using PMBus in your system increases power density and reliability of the power supply, as well as optimizing component performance and efficiency with reduced design time, risk and cost. PMBus enables you to monitor current, voltage, and temperature as well as report and log faults. Through PMBus, the designer is able to configure the IC on the fly by storing new default parameters in the nonvolatile memory, thus allowing new designs to be generated and validated in a shorter period of time.
TI supports a broad range of PMBus based DC/DC converters, point-of-load (POL) single-/multi-output and single-/multi-phase pulse-width modulation (PWM) controllers, hot swap ICs, sequencers/managers and isolated PWM controllers. With multiple options, it can be challenging to select the correct device for your application.
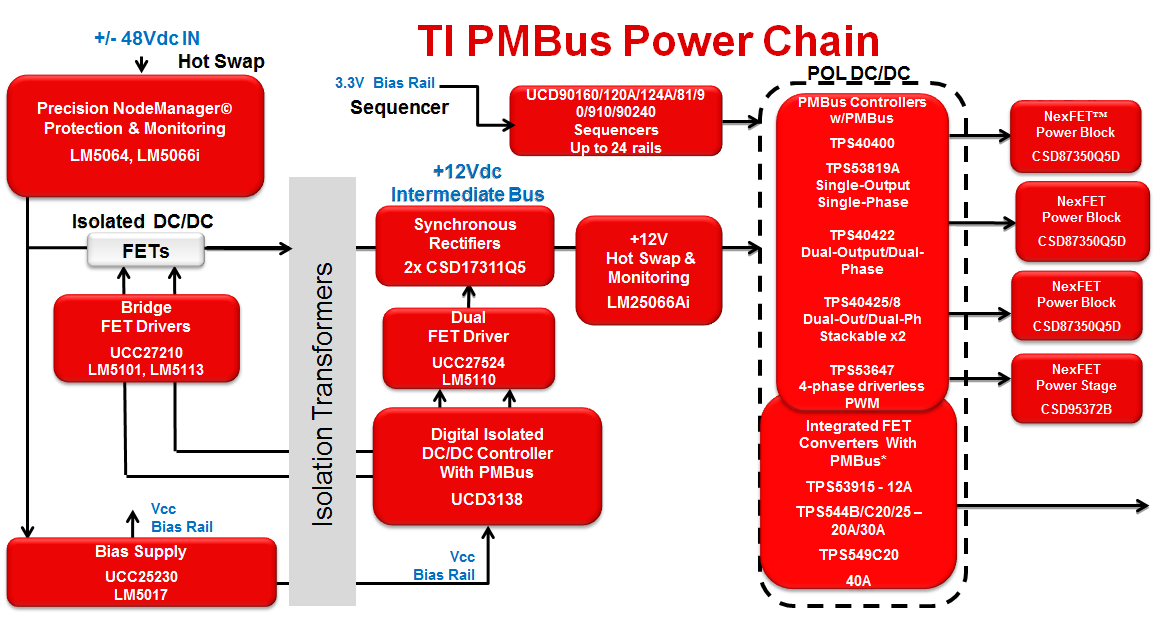 Figure 1 TI’s PMBus Power Chain
Diagram.
Figure 1 TI’s PMBus Power Chain
Diagram.TI’s PMBus controllers and converters are offered in two different control mode topologies: an analog control loop, which is often the fastest, and a digital control loop, which can add delays to the system due to its clock and proportional-integral-derivative (PID) circuitry. Many of TI’s PMBus D-CAP™, D-CAP2™ and D-CAP3™ based controllers and iFETs feature an analog control loop, which allows for faster load transient response and no loop compensation.
Integrating the driver onto the chip does not always provide the optimal power partitioning because it limits the switching frequency (Fsw) and increases power dissipation in the PWM controller. TI has many devices that support a driverless architecture, which was first implemented in TI’s multiphase PWM controllers in 2013. This architecture enabled an impressive power density increase and board area reduction (up to 3x area reduction) due to the increased switching frequency capability. It also allowed the manufacturer to heat sink the large bottom pad of the complementary power stage directly into the PCB internal ground layers for easier layout.
PMBus Examples for the Different Architectures:
Multiphase PWM controllers (driverless):
- TPS40425 and TPS40428 dual phase/dual output multiphase PWM controllers stack up to 4-phases and feature voltage mode control with feed forward. These controllers can be paired with TI’s 60A synchronous buck NexFET™ CSD95372A or CSD95378B smart power stage products. See a TI Design reference design here.
- TPS53647 TI’s first general-purpose, high-current, 4-phase, single output PMBus multiphase PWM controller for ASIC/FPGA cores. Features include auto balance, D-CAP+™ control mode and a RESET function. Together, these features enable reduced overshoot and undershoot, tight phase-to-phase current and thermal sharing, reduced output capacitor count, ease of resetting to the original boot-up voltage without power cycling, and low external component count.
Multiphase PWM controllers (with gate drivers):
-
TPS40422 dual phase, dual output multiphase PWM controller features voltage mode control with feed forward.
iFET converters (with integrated MOSFETs):
- SWIFT™ 20A TPS544B20 and 30A TPS544C20 D-CAP2 control mode converters.
- SWIFT 20A TPS544B25 and 30A TPS544C25 voltage control mode converters with frequency synchronization. See Table 1 for TI’s complete portfolio of SWIFT products.
- TPS53915 12A D-CAP3 control mode converter with a reduced set of PMBus features.
PWM controllers:
- TPS40400 PWM controller features an external power block and voltage mode control with feed forward. See Table 2 for TI’s complete portfolio of PWM controller products.
- TPS53819A D-CAP2, single synchronous Eco-mode™ buck controller with PMBus
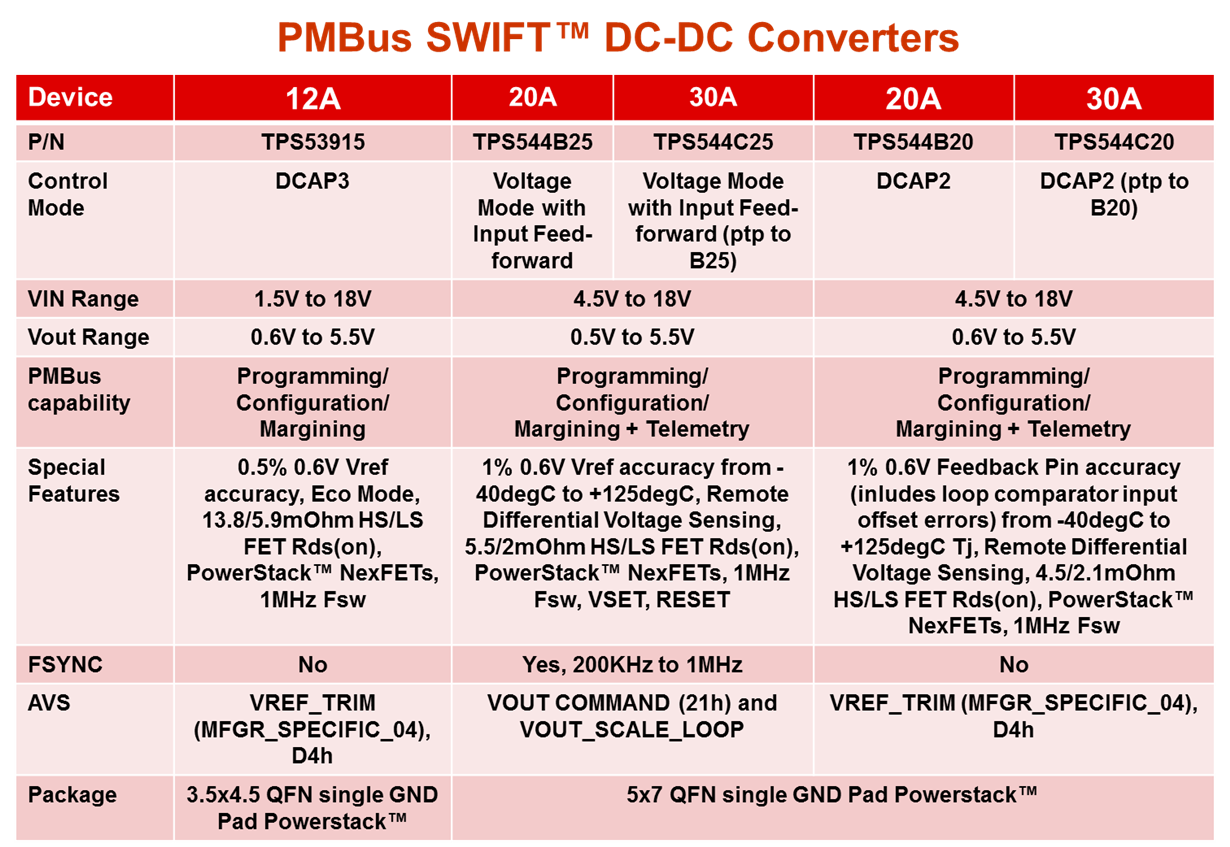
|
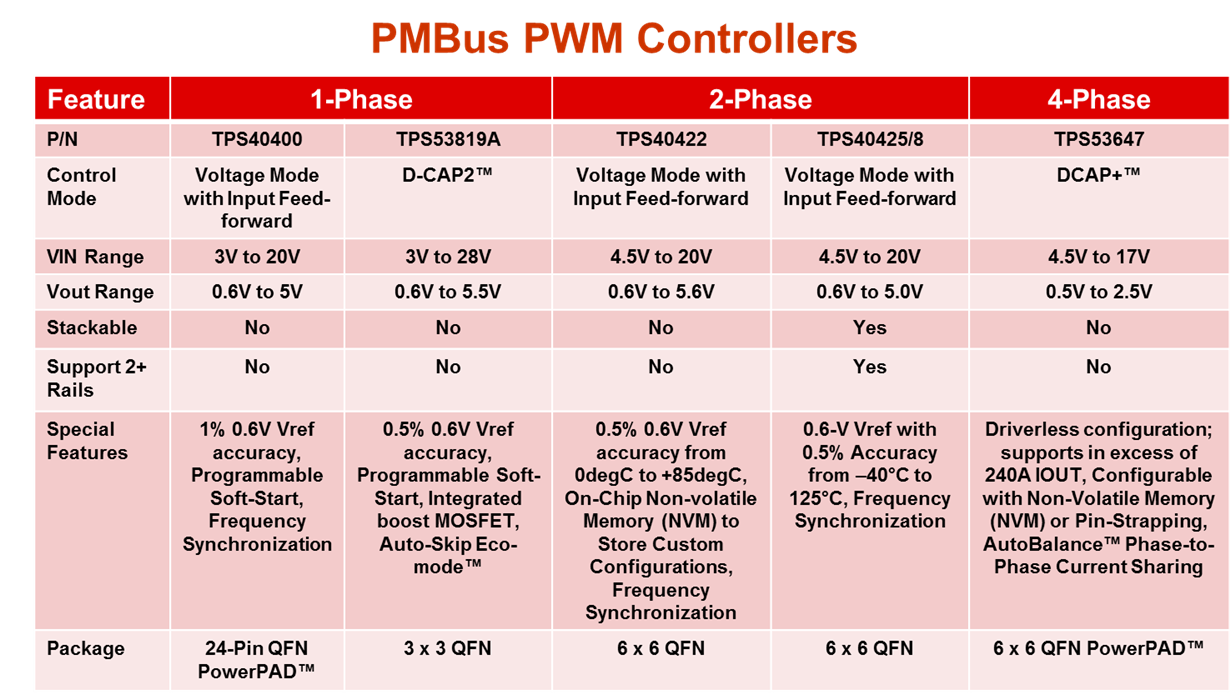 |
I hope this helps you understand the various PMBus based products that TI offers while helping you to select the correct device for your application.
Additional Resources:
- Watch the videos, “Adaptive Voltage Scaling (AVS) for High-Performance DSPs” and “Designing with PMBus™ in WEBENCH™ Design Tools.”
- Start a power supply design in WEBENCH Power Designer.
- Download the Complete PMBus Power System for Enterprise Ethernet Switches TI Designs reference design.
- Get more information about TI’s SWIFT DC/DC converters.
- Review the guide to TI’s extensive portfolio of PMBus product solutions, design tools and technical resources.