SN74ABTH18646A
- Members of the Texas Instruments SCOPETM Family of Testability Products
- Members of the Texas Instruments WidebusTM Family
- Compatible With the IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990 (JTAG) Test Access Port and Boundary-Scan Architecture
- Include D-Type Flip-Flops and Control Circuitry to Provide Multiplexed Transmission of Stored and Real-Time Data
- Bus Hold on Data Inputs Eliminates the Need for External Pullup Resistors
- B-Port Outputs of 'ABTH182646A Devices Have Equivalent 25-
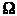 Series Resistors, So No External Resistors Are Required
Series Resistors, So No External Resistors Are Required - State-of-the-Art EPIC-IIBTM BiCMOS Design
- One Boundary-Scan Cell Per I/O Architecture Improves Scan Efficiency
- SCOPETM Instruction Set
- IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990 Required Instructions and Optional CLAMP and HIGHZ
- Parallel-Signature Analysis at Inputs
- Pseudo-Random Pattern Generation From Outputs
- Sample Inputs/Toggle Outputs
- Binary Count From Outputs
- Device Identification
- Even-Parity Opcodes
- Packaged in 64-Pin Plastic Thin Quad Flat (PM) Packages Using 0.5-mm Center-to-Center Spacings and 68-Pin Ceramic Quad Flat (HV) Packages Using 25-mil Center-to-Center Spacings
SCOPE, Widebus, and EPIC-IIB are trademarks of Texas Instruments Incorporated.
The 'ABTH18646A and 'ABTH182646A scan test devices with 18-bit bus transceivers and registers are members of the Texas Instruments SCOPETM testability integrated-circuit family. This family of devices supports IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990 boundary scan to facilitate testing of complex circuit-board assemblies. Scan access to the test circuitry is accomplished via the 4-wire test access port (TAP) interface.
In the normal mode, these devices are 18-bit bus transceivers and registers that allow for multiplexed transmission of data directly from the input bus or from the internal registers. They can be used either as two 9-bit transceivers or one 18-bit transceiver. The test circuitry can be activated by the TAP to take snapshot samples of the data appearing at the device pins or to perform a self test on the boundary-test cells. Activating the TAP in the normal mode does not affect the functional operation of the SCOPETM bus transceivers and registers.
Transceiver function is controlled by output-enable (![]() ) and direction (DIR) inputs. When
) and direction (DIR) inputs. When
![]() is low, the
transceiver is active and operates in the A-to-B direction when DIR
is high or in the B-to-A direction when DIR is low. When
is low, the
transceiver is active and operates in the A-to-B direction when DIR
is high or in the B-to-A direction when DIR is low. When ![]() is high, both the A and B outputs
are in the high-impedance state, effectively isolating both buses.
is high, both the A and B outputs
are in the high-impedance state, effectively isolating both buses.
Data flow is controlled by clock (CLKAB and CLKBA) and select (SAB and SBA) inputs. Data on the A bus is clocked into the associated registers on the low-to-high transition of CLKAB. When SAB is low, real-time A data is selected for presentation to the B bus (transparent mode). When SAB is high, stored A data is selected for presentation to the B bus (registered mode). The function of the CLKBA and SBA inputs mirrors that of CLKAB and SAB, respectively. Figure 1 shows the four fundamental bus-management functions that are performed with the 'ABTH18646A and 'ABTH182646A.
In the test mode, the normal operation of the SCOPETM bus transceivers and registers is inhibited, and the test circuitry is enabled to observe and control the I/O boundary of the device. When enabled, the test circuitry performs boundary-scan test operations according to the protocol described in IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990.
Four dedicated test pins observe and control the operation of the test circuitry: test data input (TDI), test data output (TDO), test mode select (TMS), and test clock (TCK). Additionally, the test circuitry performs other testing functions such as parallel-signature analysis (PSA) on data inputs and pseudo-random pattern generation (PRPG) from data outputs. All testing and scan operations are synchronized to the TAP interface.
Improved scan efficiency is accomplished through the adoption of a one boundary-scan cell (BSC) per I/O pin architecture. This architecture is implemented in such a way as to capture the most pertinent test data. A PSA/COUNT instruction also is included to ease the testing of memories and other circuits where a binary count addressing scheme is useful.
Active bus-hold circuitry holds unused or floating data inputs at a valid logic level.
The B-port outputs of 'ABTH182646A, which are designed to source
or sink up to 12 mA, include 25-![]() series resistors to reduce overshoot and undershoot.
series resistors to reduce overshoot and undershoot.
The SN54ABTH18646A and SN54ABTH182646A are characterized for operation over the full military temperature range of -55°C to 125°C. The SN74ABTH18646A and SN74ABTH182646A are characterized for operation from -40°C to 85°C.
The data-output functions can be enabled or disabled by
various signals at ![]() and
DIR. Data-input functions are always enabled; i.e., data at the bus
pins is stored on every low-to-high transition of the clock
inputs.
and
DIR. Data-input functions are always enabled; i.e., data at the bus
pins is stored on every low-to-high transition of the clock
inputs.
Figure 1. Bus-Management Functions
技術資料
設計および開発
その他のアイテムや必要なリソースを参照するには、以下のタイトルをクリックして詳細ページをご覧ください。
| パッケージ | ピン数 | CAD シンボル、フットプリント、および 3D モデル |
|---|---|---|
| LQFP (PM) | 64 | Ultra Librarian |
購入と品質
- RoHS
- REACH
- デバイスのマーキング
- リード端子の仕上げ / ボールの原材料
- MSL 定格 / ピーク リフロー
- MTBF/FIT 推定値
- 使用原材料
- 認定試験結果
- 継続的な信頼性モニタ試験結果
- ファブの拠点
- 組み立てを実施した拠点