-
Optimal Implementation of 25G/28G Retimers versus Redrivers in Common Applications SNLA335B september 2019 – may 2023 DS250DF210 , DS250DF230 , DS250DF410 , DS250DF810 , DS280BR810 , DS280BR820 , DS280DF810 , DS280MB810
-
Optimal Implementation of 25G/28G Retimers versus Redrivers in Common Applications
- Optimal Implementation of 25G/28G Retimers versus Redrivers in Common Applications
- Trademarks
- 1Overview of TI 25G/28G Retimers and Redrivers
- 2When to use a Retimer Versus Redriver
- 3Retimers for Common Network Interfaces
- 4Link Training Support With TI Signal Conditioning Devices
- 5Retimer and Redrivers Part Selection
- 6Revision History
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
Optimal Implementation of 25G/28G Retimers versus Redrivers in Common Applications
Optimal Implementation of 25G/28G Retimers versus Redrivers in Common Applications
This document provides application-based criteria to assist system developers in selecting between 25G/28G retimers and redrivers. Functional background and description of relevant performance parameters and features for these devices are included to facilitate part number comparison and selection. Channel insertion loss, networking standard compliance needs and link training support are all reviewed in the context of component selection of retimers versus redrivers to achieve signal conditioning and link reach extension.
Trademarks
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
1 Overview of TI 25G/28G Retimers and Redrivers
Figure 1-1 and Figure 1-2 illustrate the functional block diagrams for TI's 25G/28G retimers and redrivers. As evident from the block diagrams, the retimer and redriver have a few key functional differences.
- The retimer implements clock and data recovery (CDR) and sampler functional blocks, thus enabling it to output a retimed version of the input signal with lower jitter. The redriver on the other hand does not incorporate the retiming-CDR related functional blocks.
- The redriver implements a two-stage continuous time linear equalizer (CTLE) as its only form of receive equalization.
- In addition to CTLE, the retimer also implements a decision feedback equalizer (DFE). Thus the retimer is equipped with more enhanced post-cursor equalization function.
- The retimer incorporates additional diagnostic functions not available on the redriver, including PRBS pattern generation and checking and eye monitor functions.
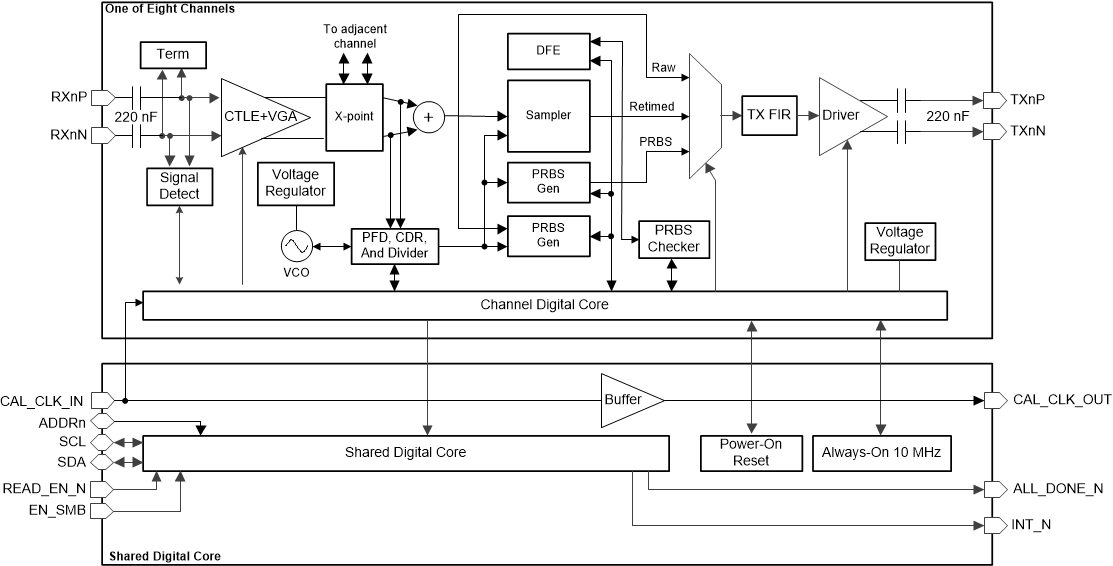 Figure 1-1 DS280DF810 Retimer Functional Block Diagram
Figure 1-1 DS280DF810 Retimer Functional Block Diagram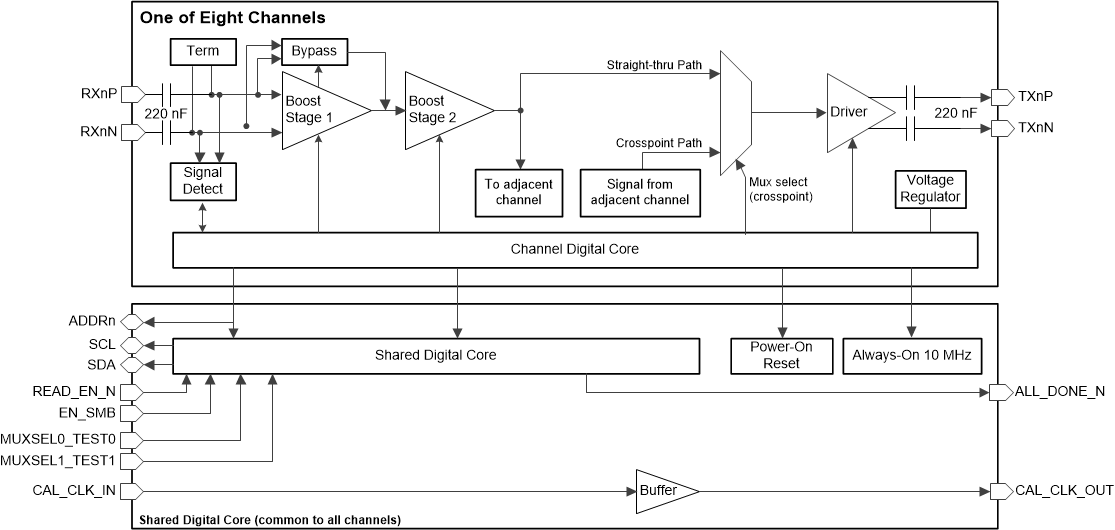 Figure 1-2 DS280MB810 Redriver Functional Block Diagram
Figure 1-2 DS280MB810 Redriver Functional Block Diagram2 When to use a Retimer Versus Redriver
Table 2-1 lists a high-level summary of chip-to-chip interface types based on their transmission channel's insertion loss at around the Nyquist frequency for 25Gbps data rate. The amount of channel loss will dictate the level of signal conditioning required for an error free chip-to-chip link. Some portion of system interconnects will have channel loss that is within the equalization compensation capability of the chips being linked together. Such links do not require signal conditioning. Links requiring a moderate amount of compensation (up to 20dB) may use a redriver instead of a retimer, in that way realizing some relative savings in power consumption and cost. Links involving transmission across a channel with very high loss require the use of a retimer.
| 25Gbps CHIP-TO-CHIP LINK CASE | RECOMMENDED SIGNAL CONDITIONING (SigCon) LEVEL |
|---|---|
| Channel loss within the chip's compensation capability | No SigCon required |
| Channel loss exceeding chip compensation by up to 20dB | TI 25G/28G redriver |
| 20dB < channel loss < 35dB | TI 25G/28G retimer |
3 Retimers for Common Network Interfaces
Referring back to Section 5, TI's 25G/28G retimer part numbers cover slightly different but over-lapping data rates, as each is targeted for specific sets of high-speed interface applications as part of a networking system. Table 3-1 lists the most common high-speed networking interface standards utilizing TI retimers along with recommendations on the most appropriate TI retimer part numbers.
| STANDARD NETWORKING HIGH-SPEED INTERFACE CASE | DATA RATE(S) INVOLVED, IN UNIT OF Gbps | SUITABLE RETIMER PART NUMBER(S) |
|---|---|---|
| CEI-25G electrical interfaces (SR, MR and LR) | 25.78125 | DS250DF810, DS280DF810, DS250DF410, DS250DF210, DS250DF230 |
| CEI-28G very short reach (VSR) interfaces | 28 | DS280DF810 |
| 25G Ethernet long reach backplane or copper cable interfaces (i.e. KR4, CR4) | 25.78125 | DS250DF810, DS280DF810, DS250DF410, DS250DF210, DS250DF230 |
| 25G/10G Ethernet front port optical host interfaces | 25.78125, 10.3125 | DS250DF810, DS280DF810, DS250DF410, DS250DF210, DS250DF230 |
| OTU4 and OTU2 telecom system front port optical host interfaces | 27.95, 10.7 | DS280DF810 |
| CPRI-7 chip-to-chip or chip-to-module interfaces | 24.33 plus legacy CPRI rates | DS250DF230 (preferred solution), DS250DF810, DS280DF810, DS250DF410 |
| 16G Fibre Channel switch chip-to-module or chip to chip-to-chip interfaces | 14.025, 8.5 and 4.25 | DS280DF810 |
4 Link Training Support With TI Signal Conditioning Devices
Link training is an optional Physical Coding Sublayer (PCS) function specified by the IEEE 802.3 Ethernet specification. It is also used by other standards such as PCIe and Fibre Channel. Link training is a state-machine based algorithm that enables two interconnected systems to converge on their respective optimal transmit equalization settings. Typically the switch ASIC (either front-port or backplane) implements the link training function. Signal conditioners such as TI retimers and redrivers are by definition mid-channel devices. In other words, these devices are placed in the middle of the ASIC-to-ASIC link to provide channel reach extension. The level of link training support offered by signal conditioners can be broken down into three categories, as described in Table 4-1.
| LINK TRAINING CATEGORY | DESCRIPTION | TI 25G/28G SigCon PRODUCTS IN CATEGORY |
|---|---|---|
| No link training support | These devices neither implement the link training digital logic nor do they pass through the link training amplitude info | DS250DF810, DS280DF810, DS250DF410, DS250DF210, DS250DF230 |
| Link training pass-through | Highly linear devices such as TI's 25G/28G redrivers will seamlessly pass through the link training amplitude info from one end to the other | DS280BR820., DS280MB810 |
| Full link training support | These devices implement the digital logic required to execute the link training process in accordance with network standards | Not supported by TI retimers or redrivers |
- Recommendation: 25G system developers requiring Link Training support may implement TI's 25G/28G redrivers for mid-channel reach extension.