SLVAF64A July 2021 – November 2022 TPS62800 , TPS62801 , TPS62802 , TPS62806 , TPS62807 , TPS62808 , TPS62864 , TPS62865 , TPS62866 , TPS62867 , TPS62868 , TPS62869 , TPSM82810 , TPSM82813 , TPSM82816 , TPSM82864A , TPSM82866A , TPSM82866C , TPSM8287A06 , TPSM8287A10 , TPSM8287A15
3 TPS62864/6/8/9: VSET/VID Pin
As previously described, VSET/VID pin is used as startup to correctly set the output voltage and the I2C address of the device. During operation, the pin can be used to select the VOUT registers for the output voltage (Low = VOUT register 1; high = VOUT register 2) (TPS62868x 2.4-V to 5.5-V Input, 4-A/6-A Synchronous Step-Down Converter with I2C Interface in QFN Package data sheet and TPS62864/6 2.4-V to 5.5-V Input, 4-A and 6-A Synchronous Step-Down Converter with I2C Interface in WCSP Package data sheet).
If the designer wants to set VSET/VID pin to a low level, then the standard configuration can be adopted as shown in Figure 3-1: it is sufficient to place a resistor connected to ground. During t_startup_delay, the R2D conversion can be performed without additional parasitics and during operation it pulls down the pin to GND.
Instead, if the designer wants to set VSET/VID pin to High level, they need to put in parallel to the resistor a driving circuit to properly drive the input.
The preferred solution is to use an external digital circuit (for example, an FPGA or an MCU) to correctly drive the pin during operation, as shown in Figure 3-1.
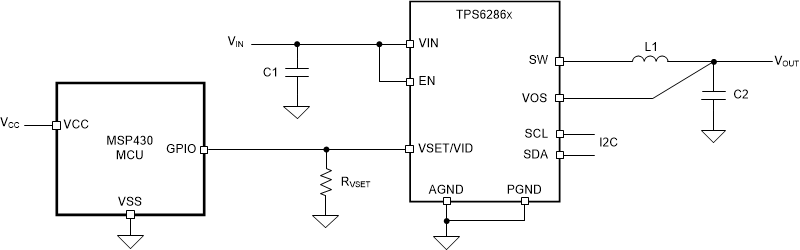 Figure 3-1 Typical Application
Schematics, VSET/VID Driving Circuit with MCU
Figure 3-1 Typical Application
Schematics, VSET/VID Driving Circuit with MCUAt startup the GPIO should be in high impedance state: VSET/VID pin sees only the resistor (plus GPIO parasitics) that sets the correct output voltage. After the startup phase, the designer can decide to pull the pin high or low according to the preferred operation changing the GPIO state (the polarization of the pin can also be switched during run time to adapt to any particular necessity).
The designer is only required to assure that the GPIO parasitics are lower than the maximum ones, as specified in section Section 2.
For example, the MSP430FR2000 data sheet specified a High-impedance leakage current of 20nA and an input capacitance of 5pF, compliant with the above specifications.
| Parameter | Test Conditions | VCC | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIT+ | Positive-going input threshold voltage | 2 V | 0.90 | 1.50 | V | ||
| 3 V | 1.35 | 2.25 | |||||
| VIT– | Negative-going input threshold voltage | 2 V | 0.50 | 1.10 | V | ||
| 3 V | 0.75 | 1.65 | |||||
| Vhys | Input voltage hysteresis (VIT+ – VIT–) | 2 V | 0.3 | 0.8 | V | ||
| 3 V | 0.4 | 1.2 | |||||
| RPull | Pullup or pulldown resistor | For pullup: VIN = VSS
For pulldown: VIN = VCC |
20 | 35 | 50 | kΩ | |
| CI,dig | Input capacitance, digital only port pins | VIN = VSS or VCC | 3 | pF | |||
| CI,ana | Input capacitance, port pins with shared analog functions | VIN = VSS or VCC | 5 | pF | |||
| Ilkg(Px.y) | High-impedance leakage current | 2 V, 3 V | –20 | +20 | nA | ||
| t(int) | External interrupt timing (external trigger pulse duration to set interrupt flag) | Ports with interrupt capability (see block diagram and terminal function descriptions) | 2 V, 3 V | 50 | ns | ||