SCDA017A September 2019 – July 2024 BQ24392 , HD3SS212 , HD3SS213 , HD3SS214 , HD3SS215 , HD3SS3202 , HD3SS3212 , HD3SS3220 , HD3SS3411 , HD3SS460 , TMUXHS4212 , TS3DV642 , TS3USB221 , TS3USB221A , TS3USB221E , TS3USB30 , TS3USB3000 , TS3USB3031 , TS3USB30E , TS3USB31 , TS3USB31E , TS3USB3200 , TS5USBA224 , TS5USBC400 , TS5USBC402 , TS5USBC41 , TUSB1042I , TUSB542
2.2 Bandwidth (BW)
Bandwidth is an important parameter to characterize the performance of many electrical systems. The bandwidth of a mux indicates the upper limit of the frequency of signals passing through the mux. The derivation was based on a low-pass filter circuit, which serves as a general model for systems exhibiting low-pass filter behavior.
The range of frequencies for which a filter does not cause significant attenuation is called the pass band, and the range of frequencies for which the filter does cause significant attenuation is called the stop band. RC low-pass filter always transition gradually from pass band to stop band. This means that it is impossible to identify one frequency at which the filter stops passing signals and starts blocking signals. Engineers need a way to conveniently summarize the frequency response of a filter, and this is where the concept of cutoff frequency comes into play.
The cutoff frequency of an RC low-pass filter is the frequency at which the amplitude of the input signal is reduced by 3 dB (3 dB reduction in amplitude corresponds to a 50% reduction in power). Thus, the cutoff frequency is also called the –3 dB frequency. The term bandwidth refers to the pass band width of a filter, and in the case of a low-pass filter, the bandwidth is equal to the –3 dB frequency (as shown in Figure 2-1)
Understanding the bandwidth capability of a signal mux helps to determine if a mux meets the performance requirements of the target application.
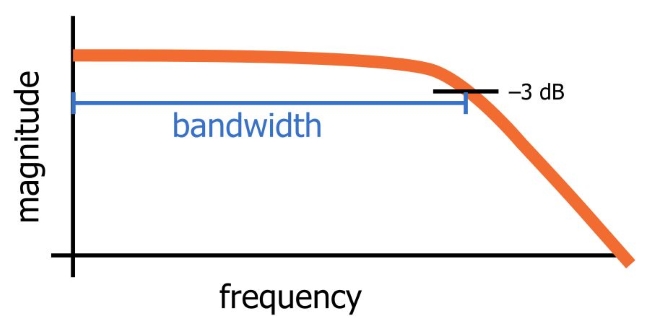 Figure 2-1 Bandwidth of Low-Pass Filter
Figure 2-1 Bandwidth of Low-Pass Filter