SLVA505A February 2012 – July 2024 DRV8800 , DRV8801 , DRV8802 , DRV8803 , DRV8804 , DRV8805 , DRV8806 , DRV8811 , DRV8812 , DRV8813 , DRV8814 , DRV8818 , DRV8821 , DRV8823 , DRV8824 , DRV8828 , DRV8829 , DRV8830 , DRV8832 , DRV8832-Q1 , DRV8833 , DRV8834 , DRV8835 , DRV8836 , DRV8837 , DRV8840 , DRV8841 , DRV8842 , DRV8843 , DRV8844 , DRV8870 , DRV8871 , DRV8872
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Factors Limiting the Maximum Output Current of a Motor Driver
- 2TI Motor Driver OCP Operation
- 3TI Motor Driver Data Sheet Ratings
- 4References
- 5Revision History
1.4.3 Copper Thickness
The thickness of the copper on the plane is crucial for PCB thermal performance. Increasing the copper thickness on the PCB can further decrease the plane’s effective thermal resistance. This can enhance the boards ability to conduct and dissipate heat leading to improved reliability and performance, as the traces can be able to safely and efficiently carry more current.
For high-power applications a copper thickness greater than 0.5-oz or 1-oz is recommended to maintain lower operating temperatures. In all TI motor driver EVM designs, the use of 2-oz copper thickness is used on top and bottom layers. In a typical 4-layer PCB design, 2-oz copper on top and bottom layer is used with 1-oz copper for the signal layers in between. A good guideline is if the copper thickness is doubled, the thermal resistance for the same sized plane is halved.
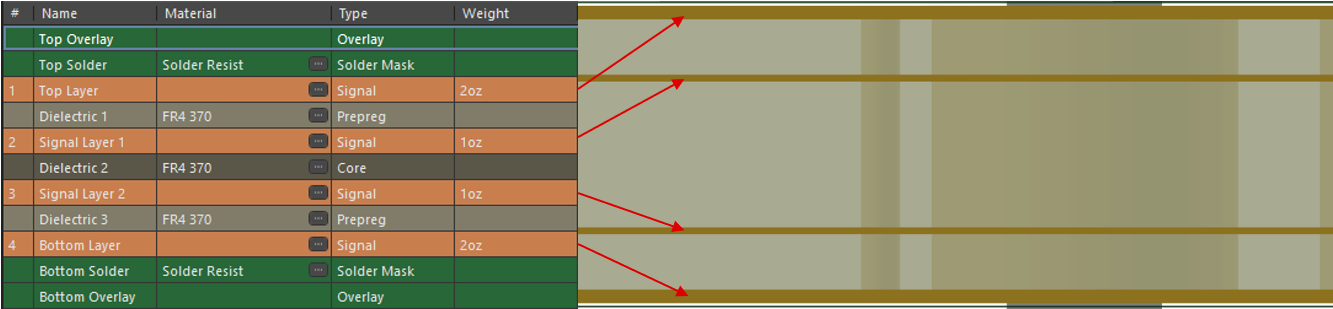 Figure 1-3 Copper Thickness Example of
4-layer EVM
Figure 1-3 Copper Thickness Example of
4-layer EVM